Lipoma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
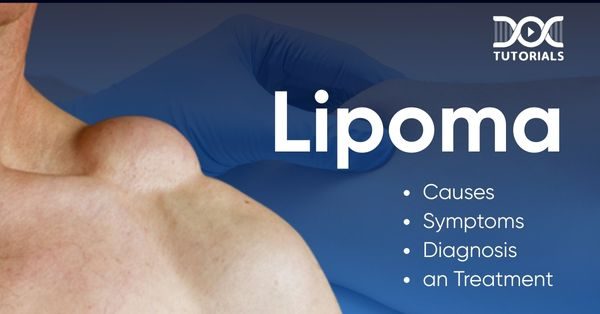
Occurring in about 1% of the population in India, lipomas are lumps of fatty tissue that occur just under the skin, most commonly among people who are in their 50s or 60s. These are painless lumps of fatty tissue that develop just under the skin.
While they are usually painless and do not pose health risks, there are instances where they may require medical intervention. It is imperative to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment of lipomas, particularly for those who will need to be able to differentiate them from dangerous conditions.
Keep reading to learn more about this condition!
What is Lipoma?
A lipoma is a soft, rounded, or oval fatty tissue lump that develops just under the skin. It is usually movable on palpation and is generally painless. Lipomas may be of any size, ranging from as small as a pea to several inches in diameter. They are most commonly located on the upper body, arms, or thighs but can be found anywhere on the body.
These soft tissue tumours are benign and develop slowly, and they do not present serious health threats. Although they are generally harmless and need not be treated, people should consider having them removed by physicians if the lipoma is irritating, painful, or indicates growth.
Where do Lipomas form?
Lipomas can grow anywhere in the human body. Although they do not develop on the muscles, brain, or other internal organs, most of them form under the skin and mainly in these places in the body:
- Arms
- Legs
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Trunk (chest and torso)
- Back
- Forehead
Causes of Lipoma
Healthcare professionals are unsure of the main causes of lipomas. However, there are several conditions that can result in the growth of lipomas in the body:
- Dercum’s Disease: It is an unusual disorder involving the formation of painful lipomas, most often found on the trunk, legs, and arms. It has also been known as adiposis dolorosa or Anders’ syndrome.
- Gardner Syndrome: It is a form of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) that results in the development of lipomas and other health issues.
- Madelung’s Disease: It is a condition which often occurs in men who consume excessive alcohol. It also goes by the name multiple symmetric lipomatosis, which leads to lipomas growing on the neck and shoulders.
- Hereditary Multiple Lipomatosis: Also referred to as familial multiple lipomatosis, it is a hereditary disorder that is transmitted through family branches.
Risk Factors of Lipoma
There are a few risk factors that may increase your chances of developing a lipoma. These include:
- Age: Lipomas are more common among people 40 to 60. Although the growths occur at any age, they are most common in this age group.
- Genetics: Genetic influences seem to have a relevant impact on the occurrence of lipomas since they usually appear in families.
- Obesity: Anyone with obesity tends to develop lipoma sooner or later.
Symptoms of Lipoma
Mentioned below are the common symptoms that may manifest if someone has lipoma:
- A Soft, Movable Lump: Lipomas are most often soft to the touch and can be easily shifted beneath the skin. They can range in size from a tiny bump to a large, easily observable mass.
- Painless or Mild Pain: Lipomas are usually not painful. However, if they compress nearby nerves, muscles, or other tissues, they can cause pain, discomfort, or stiffness.
- Feels Doughy and Slippery: When you press the lipoma, you will find it soft and doughy so that it can move freely with the pressure of the fingers.
- Stays in One Place: It remains limited and stays in a particular area because it is covered by a thin fibrous sheath that prevents it from infiltrating surrounding tissues.
- Other Symptoms: Anyone having a lipoma on or near the bowels may experience vomiting, nausea, and constipation.
Diagnosis of Lipoma
Large lipomas can be seen as bulging, appearing clearly as rounded masses on the skin surface. To diagnose a lipoma, your doctor can perform the following tests:
- A physical examination
- Biopsy to sample tissue to be analysed in the lab
- Imaging procedures, such as an X-ray, MRI, or CT scan, if the lipoma is large, has unusual features, or appears to be deeper than the fatty tissue.
Treatment Options for Lipoma
There are several treatment methods available for the management of lipomas, some of which are:
- Surgery
The most widespread way of eliminating lipomas is surgery. This is not a complicated process and is done under local anaesthesia. The surgeon removes the lump, removing the fatty tissue in the process. This method is often successful, and the chances of the recurrence of the lipoma are negligible.
- Liposuction
While treating larger lipomas, liposuction can be an option. Liposuction uses a thin tube inserted through the skin into the lipoma to remove the fat cells by suction. Liposuction is less invasive than open surgery, but there is a higher risk of remaining behind lipoma tissue, which might result in recurrence.
- Steroid Injections
In some instances, steroid injections may be used to shrink a lipoma. While this is not a permanent solution, it can reduce the size of the lump, especially when surgery is not feasible or is not desired.
Best Foods to consume for reducing Lipomas
Certain foods are believed to have a positive effect on hormonal regulation and metabolism, which can also be helpful for individuals with lipomas:
- Vegetables
Vegetables contain a high amount of nutrients, fibre, and antioxidants. They promote overall health and are believed to reduce inflammation that may exacerbate lipomas. Some ideal options include broccoli, kale, spinach, and other green vegetables.
- Turmeric
Turmeric contains a substance named curcumin, which is an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant. It can reduce body inflammation, which is also said to be associated with the development of lipomas.
- Fruits
Fruits are rich in fibre, vitamins, and antioxidants. Blueberries, raspberries, and pears are especially beneficial for people with lipomas.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids may reduce inflammation and restrict the growth of fat tissue beneath the skin. Salmon, mackerel, herring, and cod liver oil are some good sources. Being rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, these items are great to help reduce lipomas.
- Olive Oil
Olive oil is high in monounsaturated fats, which are good for the heart. It also possesses antioxidants that may reduce inflammation and help lessen lipomas.
- Green Tea
Green tea is a healthy beverage for individuals with lipomas. It is rich in antioxidants and can increase fat oxidation and metabolism, possibly aiding in decelerating the growth of lipoma.
FAQs About Lipomas
- Are lipomas and liposarcomas same?
No, lipomas are different from liposarcomas. While liposarcomas are malignant fat cell tumours, lipomas are not. Even their appearances tend to be nearly indistinguishable from each other.
- What are the types of lipoma?
Lipomas are grouped into many different subtypes, such as angiomyolipomas, angiolipomas, myelolipomas, ossifying lipomas, chondroid lipomas, spindle cell lipomas, fibrolipomas, hibernomas, pleomorphic lipomas, and neural fibrolipomas.
- How much time do lipomas take to grow?
In general, lipomas develop gradually for months or years, usually averaging between 1 to 10 centimetres in size.
- What foods must be avoided for lipoma?
It is better to avoid foods and drinks that contain a lot of sugar, such as sweets, candies, and pastries, because they can raise blood glucose levels and result in fat accumulation. One should also limit the consumption of alcohol since it can disrupt metabolic processes and trigger fat deposition, thus escalating the risk of lipoma.
- What are the complications of lipoma?
Lipomas are generally harmless and do not lead to any complications, but at times, they can be troublesome when they become large or put pressure on nerves or other tissues.
Conclusion
Lipomas are normally benign tumours that form from fatty tissues under the skin. Knowing the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments can help manage lipomas effectively. For students aspiring to a career in medicine, a thorough knowledge of lipomas and other medical conditions is important to excel in exams like NEET PG. DocTutorials offers cutting-edge learning techniques and NEET PG study materials, which enable students to acquire the expertise required to understand and remember complex medical concepts.
Latest Blogs
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…




