Gangrene: Causes, Symptoms, Types, Treatment, and More
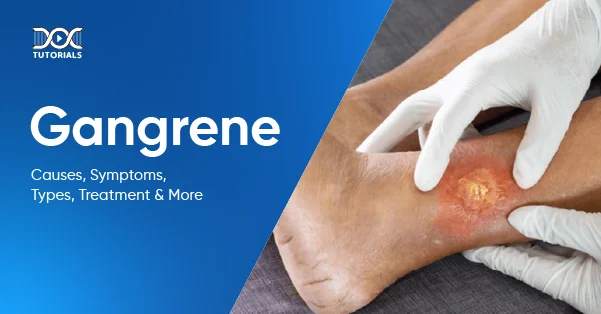
A rare but prevalent disease in India, gangrene poses a significant threat of death or can have a huge impact on the overall quality of life of those who survive. This disorder can affect the hands, limbs, and even the internal organs.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of gangrene must be done to ensure no further tissue damage and reduce the chances of amputation. For those undergoing medical exams, such as the NEET PG, it is important to know about the causes, types, and treatment of gangrene.
Want to learn more about gangrene? Continue reading!
What is Gangrene?
The term “gangrene” comes from Greek and Latin words meaning a gnawing sore or rotten tissue. It refers to the death of body tissue as a result of a severe bacterial infection or inadequate blood flow. Gangrene happens when the blood supply to a body region is cut off; tissues can no longer obtain oxygen and nutrients, resulting in their death.
Even though gangrene may affect any tissue in the body, it usually begins in the fingers, toes, hands, or feet. The infected skin turns a greenish-black colour. If left untreated, gangrene causes serious complications, spreading all over the body and even leading to septic shock or death.
Types of Gangrene
Gangrene can be divided into 6 types, each having different characteristics, causes, and treatment methods. Here are the common types of gangrene:
- Dry Gangrene
Dry gangrene takes place when a part of your body does not receive sufficient oxygen, leading to its weakening and death. It normally occurs in the feet and toes. Dry gangrene is slow in its progression and is usually observed in the initial stages of gangrene foot.
- Wet Gangrene
Wet gangrene results from infection of body tissues by bacteria. These bacteria moisten the tissues and cause them to disintegrate, thus causing tissue death. Wet gangrene leads to a foul smell and is more critical than dry gangrene because it can rapidly spread the infection.
- Gas Gangrene
Gas gangrene is caused by clostridia bacteria leading to infection, which forms gas bubbles and toxins in the infected area. This can cause the death of the tissue and is extremely dangerous as it increases the likelihood of death if left untreated.
- Internal Gangrene
Internal gangrene occurs in organs such as the intestines, gallbladder, or appendix when the blood supply to them is cut off. This can take place if the intestines twist from a weakness in the abdominal muscles. Internal gangrene is not curable if it remains untreated and can be life-threatening.
- Meleney’s Gangrene
Meleney’s gangrene is an infrequent type that often results from postoperative complications. It is also referred to as progressive bacterial synergistic gangrene.
- Fournier’s Gangrene
Fournier’s gangrene is found in the genital area and may involve both men and women, but it is more prevalent in men. It is normally a result of an infection of the urinary tract. The affected area turns red and painful with rapid progression to gangrene and tissue sloughing.
Causes of Gangrene
Mentioned below are the leading causes of gangrene:
- Reduced Blood Flow: The lack of oxygen and other nutrients in the tissues is interrupted due to the absence of normal blood flow. Such conditions, including atherosclerosis, diabetes, or peripheral artery disease, can make a person more prone to gangrene.
- Infection: Gangrene can develop more rapidly when certain types of bacteria infect damaged tissue, especially in cases of wet gangrene associated with bacterial infections.
- Trauma and Injury: Trauma, in the form of burns, cuts, and wounds, is another major cause of tissue death. In many severe cases, the blood supply may be hindered when the damaged blood vessels are involved. This is a general scenario for the development of gangrene.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgery may occasionally cause gangrene, particularly if there is a post-surgical infection or if the blood supply is restricted again. Although surgeons use an extensive range of preventive measures to reduce these risks, complications may still arise.
- Chronic Diseases: Diabetes is one of the major risk factors for gangrene, especially for the foot. People with diabetes are more prone to peripheral arterial disease and, consequently, gangrene in their lower extremities due to poor blood circulation.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Severe smoking and drinking heavily reduce blood flow and greatly increase one’s chance of suffering from gangrene.
Risk Factors of Gangrene
Here are the major risk factors that can lead to gangrene:
- Anyone having a history of a few medical conditions like arteriosclerosis, blood clots, appendicitis, hernia, Raynaud’s disease, etc.
- People having diabetes.
- Individuals consuming too much alcohol.
- People have weak immunity due to a health condition or treatment for cancer.
- Individuals who underwent recent surgical procedures.
- Anyone who has suffered from severe frostbite, a head wound, an animal bite, or a serious burn.
- People who have suffered extreme trauma and distress that led to the compression of body tissues.
- People who have received an injection of promethazine hydrochloride that resulted in tissue damage.
Symptoms of Gangrene
Gangrene can result from a bacterial infection and might lead to the following signs and symptoms:
- Inflamed and reddened skin
- Severe pain or numbness
- Pale or discoloured skin
- Chills
- Crackling sound upon applying pressure on the skin (inability to hold blood due to gas build-up in the tissue)
- Increased anxiety
- Increased heart rate and rapid breathing
- A feeling of heat or profuse sweating
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Lightheadedness
- Tight and sensitive skin
- Wounds and blisters oozing blood with foul-smelling discharge
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis of Gangrene
Diagnosis of gangrene is performed with a combination of clinical assessment and procedures. These include:
- Medical History and Symptoms: Your symptoms and medical history may lead a doctor to first suspect gangrene, such as diabetes, trauma, or infections as risk factors.
- Lab Test of Tissue or Fluid Specimen: Scrapings of tissue or fluid from the infected area can be analysed under a microscope to determine the type of bacteria involved in the infection.
- Blood Tests: If someone has gangrene, blood tests may show an abnormally high white blood cell count, which signifies an infection. A blood examination may be done to see if there is any bacterial growth to aid in diagnosis.
- Medical Imaging: Imaging methods like X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans assist in establishing the severity of gangrene. It affects the inner tissues and organs.
- Arteriogram: An arteriogram is conducted if gangrene is suspected to be caused by circulatory problems. This test uses X-rays in order to track a special dye moving through the arteries, helping the doctor to see if there is any blockage in the arteries.
Treatment Options for Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious medical condition that requires immediate treatment. Here are the major treatment methods adopted for treating this condition:
- Tissue Removal
In extreme cases of gangrene, dead tissue or body parts may need to be removed. This is referred to as debridement and can be performed with the help of surgical tools or chemicals. The primary goal is to remove infected areas and dead tissue to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Skin Grafting
Physicians can also try to restore blood flow to the damaged area. Skin grafts can repair injured tissue by employing healthy skin from a different location in the body to cover the injured site.
- Antibiotics
If bacteria are responsible for causing the gangrene, your physician may recommend antibiotics. This is administered through an intravenous (IV) injection to deliver the medicine directly into the blood veins. Some of the best antibiotics for gangrene include aminoglycoside, clindamycin, ciprofloxacin, penicillin, vancomycin, cephalosporin, and metronidazole.
- Vascular Surgery
In cases of inadequate circulation causing gangrene, vascular surgery can be recommended to increase the flow of blood to the damaged tissues.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
If anyone has gas gangrene, placing that person in a high-oxygen setting can reduce the growth of the bacteria, thus providing enough time for the healing of the skin. This method also brings oxygen to the damaged tissue for recovery.
- Amputation
If the gangrene disease has reached a severe stage, the amputation of a limb, finger, or toe is an option to help a person survive. Amputees from amputation because of gangrene may be given an artificial limb for the lost body part.
FAQs About Gangrene
- How fast does gangrene grow?
Gangrene develops at varying rates. Dry gangrene tends to grow more slowly over days to months since it occurs gradually as diseases lead to obstructions in the blood vessels. On the other hand, wet gangrene develops much more rapidly.
- What is the final stage of gangrene?
If gangrene is not treated, it can spread throughout your body and cause septic shock when bacteria get into your bloodstream. Septic shock is extremely dangerous and is a matter of immediate medical intervention.
- Is the gangrene disease reversible?
Gangrene is irreversible, but it can be controlled to stop its advancement. The earlier the treatment is started, the better the chances of a successful outcome.
- Is gas gangrene a bacteria or virus?
Gas gangrene is caused by a bacteria known as Clostridium perfringens. In addition, it can also be a result of Staphylococcus aureus, group A streptococcus, and Vibrio vulnificus.
- How much time is there before gangrene leads to death?
Gangrene may cause death within varying periods depending on the type and the cause of gangrene. Gas gangrene is especially rapid, becoming lethal within 48 hours before medical intervention. If the treatment is started on time, about 75% of the patients can survive.
Conclusion
Gangrene is an extreme medical disorder that needs urgent attention and treatment to avoid tissue loss and potential life-endangering conditions. Detection at an early stage is crucial, and knowledge of the causes, signs, and management of gangrene can greatly benefit recovery.
For NEET PG examination preparation, gaining expertise in areas such as gangrene and other vital medical disorders is critical for achievement. At DocTutorials, we offer exceptional NEET PG study materials to prepare students with the necessary knowledge and skills to crack the NEET PG exam and excel in their medical careers.
Latest Blogs
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…




