Marfan Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
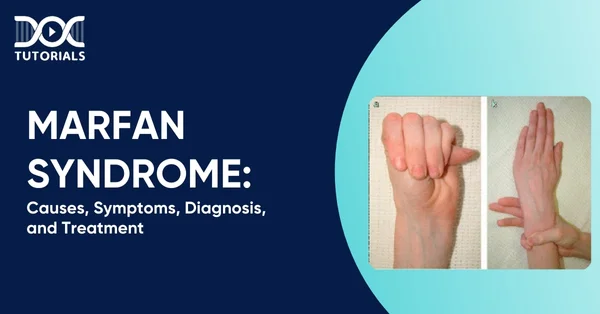
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a genetic disorder affecting the connective tissue, the fibres that give support and protect organs and other structures in the body. It most commonly damages the eyes, heart, blood vessels, and skeleton. When not well managed, this syndrome predisposes its victims to life-threatening cardiovascular complications.
Hence, timely detection and treatment are essential in enhancing the quality of life and prognosis. Students pursuing the NEET PG exam need to learn about this medical condition properly. Here is a guide covering the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment to aid aspirants in their preparation.
Keep reading!
What is Marfan Syndrome?
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder of connective tissue with autosomal dominant inheritance. This condition is caused by a mutation in the FBN1 gene on chromosome 15, which encodes the protein fibrillin-1. It is important for the elasticity and integrity of connective tissue. This syndrome affects multiple systems.
The cardiovascular system is the most impacted, particularly the aorta, which may become enlarged and weakened (aortic aneurysm), posing a risk of dissection or rupture. Other systems that are affected include the skeletal system, eyes, and lungs.
What are the Symptoms of Marfan Syndrome?
Individuals suffering from Marfan syndrome may encounter the following symptoms:
- Patients often have tall, thin bodies with unusually long arms, legs, fingers, and toes.
- A sunken chest (pectus excavatum) or a protruding chest (pectus carinatum) may develop due to abnormal chest wall structure.
- A long, narrow face with a high-arched palate and crowded teeth can be observed.
- Spine abnormalities such as scoliosis or kyphosis can occur, causing posture issues and back pain.
- Joints may be hypermobile, flexible, or weak, making them prone to dislocation.
- Flat feet are frequently seen due to altered foot structure and ligament laxity.
- Stretch marks may appear on the skin even in the absence of significant weight changes.
- Mitral valve prolapse can result in heart murmurs, palpitations, and irregular heart rhythms.
- Shortness of breath and fatigue may occur due to cardiovascular or pulmonary involvement.
- Aortic root dilation or aneurysm may lead to serious cardiovascular complications like aortic dissection.
- Eye issues are common, including lens dislocation, severe near-sightedness, and early cataracts.
- Individuals may experience a heartbeat that feels too fast, too hard, or fluttery (palpitations).
- Spontaneous pneumothorax is another complication for some patients.
- The skin may feel less elastic and more easily get irritated due to weakness in connective tissue.
- Dental crowding and narrow upper jaws can result in improper biting, leading to speech problems.
- Some patients present with the late onset of mild or subclinical symptoms, hence making early diagnosis tough without a full assessment.
- Bony overgrowth within the limbs and fingers contributes to distortion in the proportions of the body.
- Changes in connective tissue strength can affect blood vessels, making them fragile and prone to enlargement or rupture.
What Leads to Marfan Syndrome?
Marfan syndrome is triggered by a mutation in the gene FBN1, which is responsible for generating fibrillin-1, an essential protein of connective tissue. The mutation hinders the structure and function of elastic fibres and triggers excessive production of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), further softening connective tissues around the body.
The condition typically follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, indicating that a single copy of the mutated gene from either parent is sufficient to result in the syndrome.
What are the Risk Factors of Marfan Syndrome?
Below are the main risk factors for the development of Marfan syndrome:
- Marfan syndrome is mainly caused by a mutation in the FBN1 gene, which negatively impacts the synthesis of fibrillin-1 and the integrity of connective tissue.
- The advanced age of fathers may increase the likelihood of developing new genetic mutations at conception.
- The advanced age of mothers (above 35 years) may be a risk factor for spontaneous gene mutations as well.
- Familial inheritance is typical. A parent may have some mild or undiagnosed form of the disorder.
- There can be a degree of variability of the FBN1 gene in the genetic makeup of families that may produce diverse clinical manifestations.
- A positive family history presents a significantly increased risk of developing the disorder.
- One child with Marfan syndrome increases the chance of subsequent children inheriting the disorder.
- A spontaneous mutation can lead to having Marfan syndrome even with no family history.
How is Marfan Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Marfan syndrome can be challenging due to differing presentations and related conditions. Doctors usually perform the following:
- Clinical Evaluation: A physician considers some combination of clinical features affecting the patient’s heart, eyes, skeleton, and family history to determine the likelihood of Marfan syndrome.
- Heart Imaging: An echocardiogram is often the first test used to visualise heart structure and function, focusing on the aorta and heart valves.
- CT Scans and MRI: Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are other imaging options, particularly where surgery is under consideration.
- Eye Exam: A slit-lamp exam is used to diagnose lens dislocation, cataracts, or retinal detachment in eyes with fully dilated pupils.
- Genetic Testing: These tests confirm whether the patient carries a mutation in a Marfan-associated gene. Once the mutation is confirmed, family members can be screened.
How to Treat Marfan Syndrome?
Although Marfan syndrome cannot be cured, effective treatment can prevent various complications, which can help improve the quality of life and life expectancy. Here are the commonly used approaches:
- Routine monitoring
- Physical activity guidance
- Medications
- Surgery
Remember that patients will need a treatment plan based on their exact health issues associated with Marfan syndrome.
FAQs About Marfan Syndrome
- How long can you survive with Marfan syndrome?
Earlier, individuals diagnosed with Marfan syndrome could expect to survive until their mid-40s, but with recent medical progress, this has extended to the 70s.
- What should patients avoid if they have Marfan syndrome?
Individuals with Marfan syndrome are usually advised to avoid certain things, like intense physical activities, contact sports (like football and rugby), and several medications.
- What are the heart complications of Marfan syndrome?
The heart complications associated with MFS may include aortic dissection, heart valve disease, enlarged heart, and arrhythmias, and require monitoring by the doctor.
- Can pulmonary complications occur in Marfan syndrome?
Marfan syndrome can be associated with pulmonary complications that include asthma, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and even a collapsed lung as the lung tissues change.
- What are the most commonly prescribed medications for treating Marfan syndrome?
To treat Marfan syndrome, physicians often prescribe beta blockers and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) to slow the enlargement of the aorta. If a beta blocker is not recommended due to other medical conditions, the doctor may prescribe a calcium channel blocker.
Conclusion
Although uncommon, Marfan syndrome is a serious medical condition that requires early diagnosis and intervention. Correctly understanding the condition is essential for effective management, from monitoring cardiovascular health to providing genetic counselling.
NEET PG candidates must thoroughly study Marfan syndrome, as it is a clinically important disease that forms an essential part of their syllabus. To aid future physicians, DocTutorials provides high-quality study materials, concise video lectures, and more, breaking down complex genetic disorders and enabling students to excel in their academic and professional lives. Join our NEET PG courses today!
Latest Blogs
-

NEET SS Exam 2024: Analysis, Key Dates, Counselling
The NEET SS 2024 exam kicked off on March 29, 2025. Over two days and two slots, candidates across 13…
-

NEET PG Registration 2025: An Essential Guide For Exam Prep
The NEET PG registration, which is conducted online, is a crucial step in the exam process. Filling out the NEET…
-

NEET PG Syllabus 2026: A Must-Have Complete Guide for Exam Success
The NEET PG Syllabus acts as one of the foundation stones for aspiring postgraduate medical students like you who are…