Herpes: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
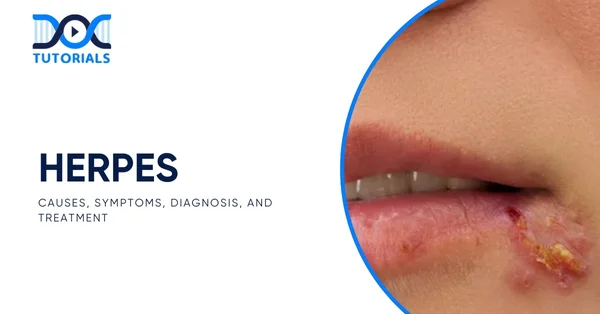
Herpes simplex is a viral disease that is contagious and develops as a result of the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) infection that is transmitted either through physical contact or sexual intercourse.
It generally causes symptoms like blistering, cold sores, itching, burning pain, as well as fever, but some people do not show any symptoms. It is a widespread condition that may go unnoticed, as this condition manifests distinct signals in various individuals.
For a NEET PG aspirant, knowledge of HSV along with its clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment is important to accurately assess and treat a patient. This guide aims to provide an overall overview of the condition to support focused preparation and clinical reasoning.
Keep reading for a detailed insight into herpes.
What is a Herpes?
HSV is a widespread viral infection that can affect many parts of the body, although it usually affects the mouth (oral herpes) and the genitals (genital herpes). It causes fluid-filled blisters to grow, which eventually break and leave a crust. People call this a herpes outbreak.
But in a lot of cases, there are no obvious signs, which makes it hard to tell if someone is sick.HSV is very contagious and spreads mostly through direct contact with the skin. When the virus gets into the body through the skin or mucous membranes, the illness starts. Once it enters the body, it begins to make copies of itself with the help of body cells.
What are the Types of Herpes?
Herpes comes in 2 forms, each of which is mainly related to infections in different parts of the body. These include:
- Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1)
HSV-1 is usually associated with infection of the upper parts of the body, mainly the mouth, the face, and the nose. It causes cold sores, blisters which are filled with fluid, rashes, and burning. HSV-1 primarily induces oral herpes, which is spread through direct contact with body fluids like the saliva of an infected individual.
- Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2)
HSV-2 is more related with genital infections. It is mostly spread by sexual contact and can cause itching, discomfort, blisters filled with fluid and genital pain. In both men and women, the symptoms can be found on the genitals, in men on the penis and in the case of women, in the vaginal area.
What are the Causes of Herpes?
Transmission of HSV infection mostly happens as a result of skin contact and direct human contact. The virus may transmit in a number of ways, even when there are no apparent signs of its infection in the infected person.
- Oral Herpes (HSV-1)
In most cases, individuals carrying HSV-1 contract the virus during infancy or early childhood. Transmission occurs through:
- Direct skin contact with someone already carrying the virus
- Sharing personal items such as utensils, lip balms, or toothbrushes that have been used by an infected person
- Genital Herpes (HSV-2)
Genital herpes is most commonly passed on through sexual contact. While HSV-2 is the typical cause, HSV-1 can also result in genital infection if transmitted through saliva during oral sex. Additionally, HSV-2 can be passed from a mother to her newborn during childbirth.
Once inside the body, the virus settles in the nerve cells, where it can remain inactive for extended periods. Even without warning symptoms, it may resume activity under some conditions. General causes of a herpes reactivation are:
- Underlying illness
- Menstruation
- Sun exposure
- Emotional or physical stress
- Surgical procedures
- Fever
What are the Symptoms of Herpes?
The symptoms of an HSV infection can differ based on the form and site of infection:
- Oral Herpes (HSV-1)
Small blisters usually form on or around the lips. Before their appearance, the skin may feel itchy, tingly, or have a burning sensation for up to two days.
- Genital Herpes (HSV-2 or HSV-1)
Blisters develop on or near the genital region. Early signs, which can develop up to 48 hours before the blisters, include fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, and a tingling or itching sensation in the affected area.
- Herpes Gladiatorum
This strain causes blisters to appear on various parts of the body, most often on the hands, face, chest, or ears.
- Herpetic Whitlow
A painful HSV infection affecting the fingers, typically resulting in blisters, discolouration around the fingernails, and noticeable swelling.
- Herpes Keratitis (Ocular Herpes)
This type affects the eyes, with symptoms such as eye discomfort or pain, sensitivity to light, a gritty feeling in the eye, and blisters near the eyelids that surround the skin.
- HSV Encephalitis
A rare but serious condition involving inflammation of the brain. Symptoms may include high fever, persistent headaches, seizures (particularly focal), and noticeable changes in behaviour or speech.
- Herpes Meningitis
This condition involves inflammation of the membranes around the brain and spinal cord. It typically presents with symptoms such as headache, fever, and sensitivity to light.
How to Diagnose Herpes?
If herpes is suspected, consulting a medical professional is essential for accurate diagnosis. Several methods may be employed to confirm the infection:
- Physical Examination
The healthcare provider may assess the affected area visually to identify any typical signs such as blisters or ulcers.
- Viral Culture
A sample is collected from an active sore or blister and analysed in a laboratory to detect the presence of the herpes simplex virus.
- Serological (Blood) Tests
A blood sample may be tested for antibodies against HSV, which helps confirm whether the individual has had a previous or ongoing infection.
- Type-Specific Antibody Testing
This test detects antibodies specific to HSV-1 and HSV-2, aiding in identifying those who may carry the virus without showing symptoms.
- Tzanck Smear
A swab or tissue sample taken from a sore is examined under a microscope to identify cellular changes commonly seen in herpes infections.
What are the Treatment Options for Herpes?
The treatment approach depends on the type of herpes and the intensity of the symptoms. Some common HSV treatment methods are:
- Cold Compresses
Applying a cold compress to the affected area often helps ease pain and reduce swelling.
- Maintaining Hygiene
Keeping the affected skin clean and dry lowers the risk of secondary infections and prevents the virus from spreading.
- Antiviral Medications
Medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are frequently prescribed. These may be taken orally or applied as creams to shorten the duration of outbreaks and lessen their severity.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Medicines like ibuprofen or paracetamol help reduce pain and discomfort during flare-ups.
- Topical Creams
Over-the-counter or prescribed creams can help relieve symptoms like burning or tingling, particularly around cold sores.
- Psychological Support
Outbreaks can lead to stress or anxiety, especially when they impact self-image or sexual well-being. Support from a qualified therapist who specialises in sexual health can offer guidance and coping strategies.
What are the Ways to Prevent Herpes?
Prevention of herpes transmission is a significant issue of concern in protecting personal and community health. The following are some reliable strategies to minimise the risk of spreading the infection:
- Avoid Close Contact During Outbreaks
It is advisable to avoid sharing personal belongings, kissing, or having sexual contact when herpes symptoms are present in an individual, as the risk of transmission is higher during this time.
- Open Communication with Partners
Those diagnosed with herpes should ensure that their partners are informed and that appropriate steps are taken together to reduce the risk of passing on the virus.
- Maintain Proper Hygiene
It is highly recommended to wash hands regularly, especially after touching affected areas. Towels and razors are personal things which one must not share.
- Adopt Safe Sexual Practices
Using protective barriers like condoms or dental dams during sexual activity can help lower the risk of infection, even when there are no visible sores.
- Use of Suppressive Medication
Healthcare providers may suggest a daily course of antiviral treatment to reduce the likelihood of passing the virus to sexual partners, particularly in cases of frequent outbreaks.
FAQs About Herpes
- Can herpes lead to major health concerns?
Herpes is not usually life-threatening but may cause significant physical discomfort and emotional stress. There are other complications that could be more severe in cases where the infection is not treated, especially among persons with weakened immune systems or during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the condition in its early stages and regular medication are vital in the management of the condition.
- Is blood donation possible with herpes simplex?
Yes, individuals diagnosed with herpes simplex can donate blood, provided certain conditions are met. They need not have an active outbreak, and any oral and genital lesions they have had recently must be dry and almost healed. Besides, they should meet all other normal blood donation eligibility criteria.
- What complications can arise from herpes simplex infection?
Herpes simplex may lead to complications when the virus spreads beyond the initial site of infection. It can cause eye infections that threaten vision, encephalitis that results in brain inflammation, and maternal transmission during pregnancy.
Conclusion
HSV is a common viral infection that can remain dormant in the body without causing visible symptoms. Despite its ability to affect uncommon areas of the body, timely identification and the use of antiviral medications help in managing outbreaks effectively and preventing complications.
As a NEET PG candidate, it is crucial to know about the causes, symptoms, and management of HSV to make an appropriate diagnosis and treatment of the patients. DocTutorials offers all-inclusive study materials and professional counsel to help you prepare for competitive exams.
Visit our NEET PG course to enhance your knowledge and improve your studies.
Latest Blogs
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…




