Fungal Infections: Types, Causes, Risk Factors Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
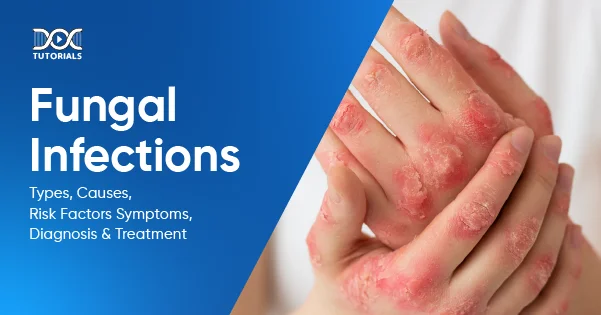
Fungal infections occur when a particular fungus grows excessively in a particular part of the body, which can affect the immune system. Studies suggest that an estimated 57 million individuals in India, equating to nearly 4.1% of the country’s population, suffer from life-threatening fungal infections.
Knowing about the types of fungal infections in detail is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Through our systematic curriculum and enhanced teaching methods, we prepare future medical professionals with all the necessary knowledge. Keep reading to learn about the symptoms of fungal infections, their types, causes, treatment methods, and more.
What are Fungal Infections?
Mycosis, or fungal infections, are caused by fungi such as yeast or mould. These infections occur on the skin or nails but can also affect the mouth, throat, lungs, and urinary tract. The immune system usually controls these fungi, preventing them from harming the body.
However, if the immune system is weak or the body balance is disrupted, these fungi can reproduce and cause infections. There are different types of fungal infections, each manifesting various symptoms such as itching, redness, and rashes.
Types of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections vary from mild to severe, depending on the kind of fungus and the part of the body that is infected. Each has specific characteristics, signs, and risk factors. Being aware of the various types of fungal infections is important for early detection and treatment:
- Superficial Fungal Infections
Superficial fungal infections usually target the skin, nails, and mucous membranes, resulting in a variety of conditions that can range from skin discolouration rashes to irritation. Fungal skin diseases and infections common in this group include:
- Ringworm (Dermatophytosis): Fungi are caused by dermatophytes and infect the skin, hair, and nails. Well-known as athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), jock itch (tinea cruris), and scalp infection (tinea capitis), others may infect the face and hands.
- Candidiasis: Due to Candida species (most commonly Candida albicans), this fungus infects mucous membranes and skin, causing oral thrush, vaginal yeast infection, and diaper rash.
- Tinea Versicolour (Pityriasis Versicolour): A Malassezia fungal infection that causes skin colouration and is usually noted as patches of lighter or darker skin.
- Onychomycosis: Fungal infection of the nails, resulting in discolouration, thickening, and cracking of fingernails and toenails.
- Subcutaneous Fungal Infections
Subcutaneous fungal infections are located deeper in the skin, usually as a result of an injury or break in the skin, often through contact with plants or soil. Infections are more prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions. Some examples are:
- Chromoblastomycosis: A long-term skin infection caused by a number of fungi, resulting in thickened, wart-like lesions on the skin.
- Eumycetoma: Typically occurring on the feet, eumycetoma causes painful swellings, abscesses, and discharge from infected tissue.
- Sporotrichosis (Rose Gardener’s Disease): Sporothrix fungi cause sporotrichosis, which usually follows an injury from a thorn or plant. The condition produces painful ulcers and nodules on the skin.
- Deep Fungal Infections
Internal organs such as the lungs, blood, and brain are attacked by deep or invasive fungal infections. Infections of this type are more serious and can be fatal, particularly in people who have weakened immune systems. Common deep fungal infections are:
- Histoplasmosis: Caused by Histoplasma and tends to affect the lungs but can spread to other organs of the body, such as the brain and liver. It occurs most frequently in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys.
- Cryptococcosis: Caused by Cryptococcus species, the infection initially begins in the lungs but may extend to the brain, leading to meningitis, especially in immunocompromised patients.
- Aspergillosis: It is an infection caused by Aspergillus, which can occur in the lungs and elsewhere in the body, causing chronic pulmonary infections or invasive forms such as aspergilloma (fungus ball).
- Blastomycosis: Blastomyces fungus invades the lungs, bones, skin, and rarely the brain or spinal cord.
- Invasive Candidiasis: Severe infections in organs like the heart, eyes, brain, or bones can be caused by several Candida species.
- Mucormycosis: A potentially fatal infection by moulds belonging to the Mucoraceae family can involve several organs, such as the sinuses, lungs, intestines, and brain.
- Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PJP): Pneumocystis jirovecii is the causative fungus of this infection, which mainly affects the lungs, especially in immunocompromised patients.
Causes of Fungal Infections
Fungal infection is a condition that may occur to anybody. Here are the major causes of this condition:
- Exposure to Fungi
Fungi grow well in warm, moist conditions and are present in areas such as locker rooms, public showers, poorly ventilated areas, and dirty surfaces. Direct contact with dirty surfaces, soil, or animals can cause fungal infections, especially in areas where moisture and heat create a perfect breeding ground for fungal growth.
- Weakened Immune System
Patients with weakened immune systems are more likely to acquire fungal infections. HIV/AIDS, cancer therapy, or the administration of immunosuppressive medication reduces the body’s immunity power to fight off fungal pathogens. As a result, fungi can freely develop, and serious systemic infections may occur.
- Use of Antibiotics
Long-term or heavy use of antibiotics may upset the body’s normal balance of microorganisms. Antibiotics will destroy good bacteria that naturally prevent the overgrowth of fungi such as Candida. Without these good bacteria, fungi can grow and lead to infection, particularly in the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and genital areas.
- Chronic Conditions
Individuals with chronic illnesses such as diabetes, particularly those with poorly managed blood glucose levels, are more susceptible to fungal infections. High blood glucose provides a body environment that promotes the growth of fungi, especially infections such as candidiasis, which often occurs in the skin and mucous membranes.
- Poor Hygiene
This is one of the major causes of fungal illnesses. Poor hygiene habits, especially in hot and humid conditions, may lead to an increased risk of contracting fungal infections. For example, not keeping skin clean, wearing the same undergarment regularly, and sharing personal items may allow dermatophytes or yeasts to grow and thrive in humid conditions.
- Travel to Fungal-Rich Environments
Travel to areas with overgrowth of fungi or outbreaks exposes a person to causative agents of fungal infections. Fungi such as Histoplasma, Coccidioides, and Blastomyces, which exist in some geographic locations, infect people upon inhalation, particularly in areas with soil disturbance or building sites.
- Dermatophytes and Yeasts
Dermatophytes are fungi that target the skin, hair, and nails. They consume keratin, a protein present in these tissues, and live in wet conditions. Yeasts such as Candida exist naturally on the body and normally do not create issues but tend to overgrow in some circumstances, causing itching, redness, and even severe infections.
Risk Factors of Fungal Infections
If you have one or more of these risk factors, there is a high chance that you might suffer from a fungal infection:
- Stem cell transplantation
- Organ transplantation
- Corticosteroids
- Being hospitalised for an extended period of time
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections can occur in different parts of the body, and their symptoms may differ significantly depending on the infected area. Early diagnosis of the symptoms ensures timely treatment and avoids the multiplication of the infection. Below are the frequent symptoms of different types of fungal infections and their appearance in the body.
- Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections are one of the most prevalent and observable among all other types. These are noticeable for their clear symptoms, including itching, redness, and even rashes. Some of the most common fungal infections on the skin are as follows:
- Athlete’s Foot: A very common skin fungus infection that typically occurs in the skin between the toes. The infected skin tends to be red and moist, and you may see peeling or fissured skin that burns or itches. The athlete’s foot should be treated as soon as possible since it can infect other areas of the body or other people.
- Ringworm: The rash is most often reddish and circular, with a clear centre of skin that has a ring-like appearance. Scaly and terribly itchy skin are common symptoms of this rash. Ringworm can be highly contagious, and to avoid its transmission, it must be treated with antifungal ointments or as prescribed by medications.
- Nail Infections
Fungal infections may also attack the fingernails and toenails, causing alterations in the appearance and form of the nails. These infections of the nails require immediate medical intervention, or else it could be fatal. The common symptoms of nail fungal infection are:
- Discolouration: The diseased nails may turn yellow, brown, or white. The discolouration is usually one of the earliest visible manifestations of a fungal infection in the nail.
- Thickening: The nails can become thicker than normal and hard to cut or wear. Thickened nails may also be painful, especially when wearing shoes.
- Brittleness: Diseased nails can become brittle, break off easily, and crumble, leading to further discomfort.
- Shape Changes: With time, if the infection persists, it can cause the nail to change shape, or it may start to become detached from the nail bed. This results in a disfigured appearance and discomfort, especially with the wearing of shoes or in daily activities.
- Systemic Infections
In serious infections, fungi infect deeper tissues and get into the bloodstream, leading to systemic infections. Systemic fungal infections are riskier and need prompt medical intervention. A systemic fungal infection presents with the following symptoms:
- Fever and Chills: These are general symptoms that the body is invaded by an infection. If a fungal infection has entered the bloodstream, the immune system of the body can produce fever and chills as it attempts to fight the infection.
- Problems in Breathing: If the infection is in the lungs, patients may have shortness of breath, coughing, and chest pain. This is usually experienced in systemic fungal infections such as Histoplasmosis or Coccidioidomycosis.
- Fatigue: Systemic infections are associated with a general sense of tiredness or weakness as the body reallocates energy to combat the fungal infection.
Treatment of Fungal Infections
Treating fungal infections or diseases caused by fungi depends on their location and seriousness. Here are some notable treatment options:
- Topical Treatments
For nail or skin infections, physicians typically prescribe antifungal ointments, creams, or lotions that you directly have to apply to the infected areas. They function by destroying the fungus or halting its spread.
Some common examples of topical medicines are Clotrimazole, Ketoconazole, and Terbinafine. Be careful to follow directions, like applying them for several weeks to effectively get rid of the infection. These are quite accessible, available over the counter or by prescription.
- Oral Medications
If the infection is more severe or does not improve with the use of ointments, you are recommended to see a doctor who may prescribe oral medications. Many oral medications available in tablets, capsules or liquids work effectively to heal fungus-affected areas in your body.
The key examples of oral medications for fungal skin infections and other diseases are Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Griseofulvin, etc. Oral antifungal pills are particularly good for persistent nail infections or ones that have aggravated deeply. These will be prescribed by a physician and monitored for side effects.
- Home Remedies
Aside from treatments in the clinic, some home care routines can also increase your recovery rate from fungal diseases. Cleaning and drying the infected area is essential, as fungi spread in moist environments.
You can also gently rub the area using antibacterial soaps and dry it thoroughly. Wearing loose-fitting clothes daily can also dissipate moisture and reduce the impact of fungal infections.
FAQs about Fungal Infections
- What are the common signs of a fungal infection?
The common symptoms of fungal infections are itching, redness, scaling, rashes, coloured skin, thick and brittle nails, and abnormal discharge.
- What are the types of treatment for fungal infections?
Depending on the type and location of the infection, fungal infections are mainly treated with creams, gels, sprays, oral drugs, or IV infusions.
- Which form of fungal infection is the most critical?
The most serious forms of fungal infections result from Aspergillus, which causes aspergillosis and primarily occurs in those with lung disease or compromised immune systems. Candida, the cause of candidiasis or thrush, is another severe issue.
- How long does it take for a fungal infection to heal?
Itching due to fungal issues may clear up in a few days after treatment; however, discolouration and scaling of the skin can take several weeks to disappear. More severe infections usually take longer to heal.
- What hygiene practices can help prevent fungal infections?
To avoid fungal infections, stick to these hygiene guidelines:
- Wash hands regularly, especially after exposure to animals or humans
- Avoid sharing your towels with others or using their towels
- Maintain dry and clean skin, particularly in the folds
- Use clean contact lenses
- Keep your nails clean
- Change undergarments regularly
- Use footwear in locker rooms, community showers, and public baths
- Sanitise equipment in the gym before and after usage
Conclusion
Fungal infections are frequent but serious medical issues that can occur in different parts of the body, from superficial cutaneous infections to life-threatening systemic infections. Prompt diagnosis and proper treatment are important to effectively control these infections. For students preparing for the NEET PG exam, Doctutorials provides an advanced curriculum and full-fledged NEET PG study materials. Join DocTutorials today and take your medical studies to the next level!
Latest Blogs
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…




