Understanding Umbilical Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Explained
Umbilical hernia affects 10-20% of newborns and also adults, especially those with obesity or prior pregnancies. While in most cases, it is harmless, it can lead to hernia complications if left untreated.
Knowing what an umbilical hernia is, its causes, and treatment options is important—not just for those affected but also for medical students looking to widen their knowledge.
Keep reading!
What is an Umbilical Hernia?
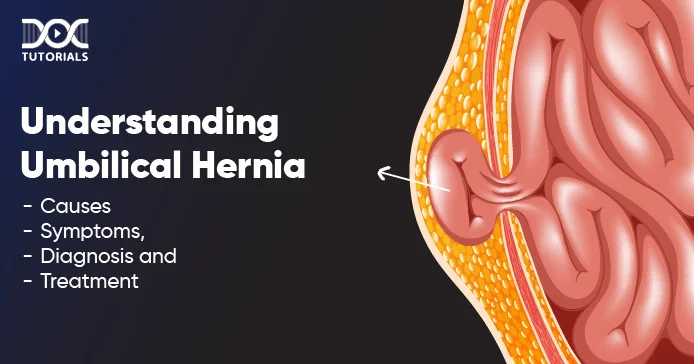
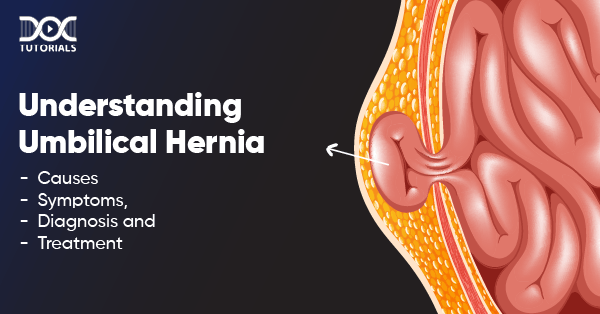
An umbilical hernia is when part of the intestine, abdominal lining or fluid pushes through a weak spot near the belly button. It appears as a bulge that gets more noticeable when you strain, cough or cry. People who can get these are:
- Infants: Common in newborns, especially premature or low birth weight babies. Resolves by age 5.
- Adults: Less common but can occur due to pregnancy, obesity or repeated abdominal strain.
Most are harmless, but some can lead to hernia complications like obstruction or strangulation. See a doctor if symptoms worsen.
What Causes an Umbilical Hernia?
The causes vary depending on the age group and different risk factors for infants and adults:
Causes in Infants
During pregnancy, the umbilical cord goes through an opening in the baby’s abdominal muscles. Normally, this closes after birth. If the muscles don’t fully join, a small umbilical hernia may appear, and tissue or part of the bowel can protrude. This is common in newborns and may resolve as they grow.
Causes in Adults
In adults, pressure on the abdominal wall can cause a hernia over time. Factors that increase this pressure are:
- Obesity, which puts strain on the abdominal muscles
- Multiple pregnancies, which stretch the abdominal wall
- Fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
- Past abdominal surgery, which weakens muscle tissue
- Long-term peritoneal dialysis, which is used for kidney failure
These conditions can create weak points where the intestine or fatty tissue can protrude. Some cases are mild, while others can lead to hernia complications.
What are the Symptoms of an Umbilical Hernia?
Check out the symptoms of umbilical hernia below:
Symptoms in Children
In children, the bulge appears when they cry, laugh or defecate. It can disappear when they lie down or are at rest. A small umbilical hernia in children is usually painless.
Symptoms in Adults
Adults with umbilical hernia will experience mild discomfort, pressure or a dull ache around the hernia area. Pain gets worse with activities that increase pressure on the abdomen.
While most umbilical hernia symptoms in adults are mild, here are signs that need urgent care:
- A bulge that becomes red, dark or firm
- Sudden or worsening abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting or blood in stool
These are signs of hernia complications, such as strangulation, which need immediate medical attention.
How is an Umbilical Hernia Diagnosed?
A doctor can diagnose an umbilical hernia by conducting a physical exam. They will evaluate the bulge near the belly button and see if any abdominal contents (intestines or fat) are stuck inside the hernia sac.
Tests to Detect Complications
If a doctor suspects complications, they may order tests such as:
- Abdominal Ultrasound – To view the hernia and rule out obstructions.
- X-ray – To check for blockage if the hernia is bowel related.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan – To view the abdominal wall and internal structures.
- Blood Tests – If there is concern about intestinal blood flow.
Early diagnosis is key to preventing complications.
What are the Treatment Options for Umbilical Hernia?
Umbilical hernia treatment depends on age, size, and symptoms:
- In infants, small hernias will close on their own by 2 years of age, and no intervention is required.
- However, if the hernia persists, grows or is causing discomfort, medical attention may be needed.
When is Surgery Needed?
A doctor may recommend surgery if:
- The hernia is bigger than 1.5 cm in diameter in children over 2 years old.
- The intestines are stuck inside the hernia sac and can’t move.
- There is pain, skin discolouration or other umbilical hernia symptoms.
- The hernia is present even after the child is over 5 years old.
Umbilical hernias in adults rarely go away on their own and are more likely to cause complications. If the hernia is painful or getting bigger, surgery is usually advised.
Umbilical Hernia Surgery
Umbilical hernia treatment without surgery in adults is not recommended as it will get worse over time. Surgery is a simple procedure that takes 20-30 minutes, and most patients can go home the same day.
The following procedures are conducted during the surgery:
- A small incision is made near the belly button hernia site.
- The herniated tissue is pushed back into the abdomen.
- The abdominal wall is stitched closed.
- In adults, a mesh may be used to reinforce the weak area to prevent recurrence.
Recovery and Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling and tenderness. Managing pain with medication and avoiding heavy activity can help in recovery. Doctors may advise:
- Keeping the dressing clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Wearing hernia support garments for extra comfort.
- Avoiding heavy lifting and intense physical activity for a few weeks.
Most times, surgery is effective, and patients recover fully within a few weeks. However, following postoperative care instructions is crucial to ensure proper healing and prevent recurrence.
Who is at Risk for an Umbilical Hernia?
An umbilical hernia can happen to anyone at any age, but certain factors increase the risk. While infants are more common, adults with specific health conditions or lifestyle factors are also prone to this condition.
Key risk factors include:
- Age
Infants, especially preterm babies, are at higher risk of getting an umbilical hernia. Their abdominal muscles are not fully developed at birth, making them more susceptible to this condition.
- Obesity
People with excess weight are at higher risk, as extra pressure on the abdominal wall weakens the muscles over time. Children and adults with high Body Mass Index (BMI) are more likely to get umbilical hernia than those in the healthy weight range.
- Chronic Coughing
Prolonged coughing puts extra pressure on the abdominal muscles and can cause hernia formation. Over time, the pressure can enlarge a small umbilical hernia and increase the risk of complications.
- Pregnancy
Pregnant individuals are at higher risk as the growing uterus stretches the abdominal wall. Those with multiple pregnancies are more prone, as repeated stretching can weaken the muscle layers and cause hernia formation.
What are the Potential Complications of Umbilical Hernia?
Most umbilical hernias are harmless, but complications can occur if the bulge gets stuck. Check them out below:
- Strangulation and Tissue Damage
A small umbilical hernia gets stuck, and the blood supply to the intestines is cut off. In extreme cases, this can cause tissue death and infection. This is rare in kids but more common in adults.
- Intestinal Blockage
A hernia that blocks the intestines will cause pain, nausea, and digestive issues. Adults with umbilical hernia are more likely to have blockages and may need emergency surgery.
- Life-Threatening Infections
When the blood flow is completely cut off, the tissue can turn gangrenous, and infections can spread throughout the abdominal cavity. Immediate medical help is crucial to avoiding complications.
FAQs about Umbilical Hernia
- How serious is an umbilical hernia?
Most umbilical hernias are not serious but need to be checked by a doctor. They are common in infants and young children but can also occur in the case of adults.
- Can you live with an umbilical hernia?
In adults, umbilical hernias don’t go away on their own. Without treatment, they can get stuck (incarcerated) and cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and bowel issues.
- When is the right age for umbilical hernia surgery?
90% of umbilical hernias in children close on their own by age 4-5. Surgery is usually done if it persists beyond this age.
- What should you avoid if you have an umbilical hernia?
To prevent worsening, avoid heavy lifting, straining, and any activity that puts pressure on the hernia.
- What causes an umbilical hernia in adults?
Common causes are obesity, pregnancy, chronic coughing, heavy lifting, and past abdominal surgery, all of which increase abdominal pressure.
- What are the warning signs of a hernia emergency?
Seek immediate medical help if you have:
- A painful bulge that doesn’t go away when lying down
- Increasing pain
- Nausea, vomiting or bloating
- Trouble passing stool
- Fever or rapid heart rate
Conclusion
An umbilical hernia isn’t always a big deal, but its impact varies across individuals. In kids, it goes away on its own, while in adults, it carries more risks. Even small umbilical hernia symptoms should be monitored to prevent further issues. If you have pain or signs of hernia complications, get medical help immediately.
Knowing umbilical hernia causes, symptoms, and treatments will help you stay informed about your health. Also, if you are a NEET PG aspirant, you will find many more such medical topics on DocTutorials NEET PG courses. We have study materials, video courses, and a Quick Revision Program (QRP) to help you crack your exams.
Enroll in our courses today and secure your future as a medical professional!
Latest Blogs
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…