Haemorrhoids: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
According to a recent study, almost 11% of the Indian population suffers from haemorrhoids or piles. This condition can arise from a number of factors like age, chronic constipation, poor dietary choices, and more. Although uncomfortable, haemorrhoids or piles do get better on their own if one adopts the proper remedies.
Thus, it is crucial to understand the types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for haemorrhoids to effectively manage this medical condition. Also, if you are a medical aspirant or a healthcare professional, learning in detail about piles is crucial for expanding your knowledge base and providing care to patients.
Keep reading!
What are Haemorrhoids?
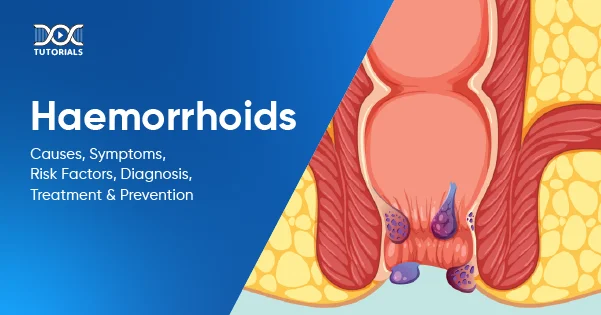
Haemorrhoids are swollen veins which are found both inside and on the outside of the anus and rectum. These swollen veins may cause itching, pain, and bleeding. Also known as piles, haemorrhoids are categorised as either internal, which lie inside the rectum, or external, which form under the skin around the anus.
What are the Different Types of Haemorrhoids?
The classification of haemorrhoids depends on the site where the engorged vein arises. Check them out below:
- External Haemorrhoids
These are swollen veins that appear under the skin around the anus, which is the end part of the large intestine and facilitates the excretion of stool. External haemorrhoids cause itching and soreness, and they can often cause bleeding. Although this problem is not threatening, it is capable of creating severe pain and inflammation.
- Internal Haemorrhoids
This category consists of engorged veins that occur inside the rectum, which is the portion of the gastrointestinal tract between the colon (large intestine) and the anus. Internal haemorrhoids can cause bleeding but are usually not painful.
- Prolapsed Haemorrhoids
Prolapsed haemorrhoids can cause severe pain or bleeding. Both internal and external haemorrhoids can become prolapsed or extend and protrude out of the anus.
- Thrombosed Haemorrhoids
When a blood clot has formed, an external haemorrhoid may be blue or purple in colour. This condition is known as thrombosis or thrombosed haemorrhoids.
What are the Causes and Risk Factors of Haemorrhoids?
Although medical practitioners have not fully discovered why haemorrhoids appear, they might occur because of the following risk factors:
- Ageing: Haemorrhoids are largely prevalent in people between 45 and 65, yet they may affect younger adults as well as children.
- Chronic Constipation: People suffering from chronic constipation habitually put pressure on the blood vessel walls of the rectum and anus for bowel movement. This often leads to haemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy: The increased pressure of the developing foetus and the uterus during pregnancy compresses the pelvic region and results in haemorrhoids in around 35% of pregnant individuals.
- Diarrhoea: Frequent diarrhoea has the potential to cause the growth of haemorrhoids.
- Diet: A diet that lacks adequate fibre could be responsible for the growth of haemorrhoids.
- Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet, is a possible risk factor that can cause haemorrhoids.
- Heavy Exercises: Heavy exercises and weight lifting on a repeated basis may be contributing factors leading to haemorrhoids.
- Weight: Too much obesity can cause haemorrhoids, possibly because of increased intra-abdominal pressure.
What are the Symptoms of Haemorrhoids?
Internal haemorrhoids usually do not show any symptoms. You might notice blood in your stool, on the toilet tissue after you have wiped, or in the bowl.
Symptoms of prolapsed haemorrhoids can include:
- Pain, especially with bowel movements
- Hard lumps near the anus
External haemorrhoids can be symptomatic and appear with:
- Pain while sitting
- Rectal bleeding
- Itching in the anus
- Swelling
Lastly, the symptoms of thrombosed haemorrhoids can include:
- Severe pain
- Itching
- Bleeding
How is the Diagnosis of Haemorrhoids Performed?
A healthcare provider diagnoses haemorrhoids by evaluating the symptoms and performing a physical examination. Other procedures may involve:
- Digital Rectal Examination: The doctor places a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to feel for dilated veins.
- Anoscopy: The medical practitioner uses an anoscope, a lighted tube, to examine the lining of the anus and rectum.
- Sigmoidoscopy: The doctor uses a sigmoidoscope, a lighted tube that contains a camera, to see the inside of the lower portion of the colon (sigmoid) and the rectum. Sigmoidoscopy is classified into two types: flexible sigmoidoscopy and rigid sigmoidoscopy (proctoscopy).
What are the Treatment Options for Haemorrhoids?
Although haemorrhoids may usually heal with lifestyle changes, in certain cases, additional medical care is required. Some common treatments for haemorrhoids vary by severity and kind and can be grouped into the following:
Home Therapies
- Hydration: Sufficient fluid intake softens the stools and reduces pressure, thus lessening the symptoms of haemorrhoids.
- Topical Creams: External haemorrhoid pain may be relieved by over-the-counter (OTC) creams that reduce swelling, itching, and irritation.
- Fibre Supplements: Supplements containing fibre like methylcellulose and psyllium can help relieve constipation, thus reducing the pressure on the anus and decreasing the chances of haemorrhoids.
- Cold Compress: Ice or a cold compress applied to the area can possibly alleviate pain and swelling.
- Warm Water Bath: Taking a warm water bath in a tub while seated can bring relief from pain and inflammation.
Medications
- Zinc Oxide: Zinc oxide creams assist in minimising irritation and itching.
- Witch Hazel: Its anti-inflammatory and astringent properties provide relief from haemorrhoid pain, itching, and burning sensations.
- Lidocaine: Lidocaine creams or suppositories give relief from haemorrhoid pain.
- Painkillers: OTC painkillers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may assist in alleviating pain from haemorrhoids.
Non-surgical Treatments
- Rubber Band Ligation: A process that involves the use of an elastic band to encircle the haemorrhoid and slow down the blood supply, making it shrink.
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of a solution into the haemorrhoid to form scar tissue that shuts off the blood supply, making it shrink.
- Electrocoagulation: This technique uses electric current to prevent the blood flow to a haemorrhoid.
- Infrared Coagulation: In this method, a small probe is inserted into the rectum to transmit heat and reduce the pain of the haemorrhoid.
Surgical Treatment
- Haemorrhoidectomy: This is a surgical technique that helps eliminate large or prolapsed haemorrhoids.
- Stapling: In this method, a stapling device is utilised to eliminate an internal haemorrhoid or pull a prolapsed internal haemorrhoid inside the anus and hold it in position.
What are the Prevention Tips for Haemorrhoids?
Lifestyle modifications can lower the risk of haemorrhoids. Here are some common prevention tips:
- Have A Balanced Diet: Eat plenty of fibre-containing foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to soften stools. Adequate water intake and taking over-the-counter fibre supplements can also prevent constipation, thus reducing the chances of haemorrhoids.
- Visit The Bathroom When Required: Constantly holding back stool may lead to constipation and worsen the risk of having haemorrhoids. Hence, go to the bathroom whenever required.
- Maintain Activity Levels: Exercise daily to regularise bowel movements and keep the possibility of haemorrhoids at bay.
- Maintain Normal Weight: Maintain a standard body weight, as obesity can increase the risk of haemorrhoids.
FAQs About Haemorrhoids
- How long will it take for a haemorrhoid to heal?
Although most haemorrhoids improve in a few days to weeks with self-care and home remedies, some may last longer or become chronic. If haemorrhoids have lasted over a week or two, it is best to see a doctor.
- Are piles dangerous?
Piles do not normally cause serious problems, but in some cases, they can lead to complications. External piles can become inflamed and swollen, resulting in the formation of ulcers. Additionally, skin tags can occur when the inside of a haemorrhoid contracts, but the skin remains.
- How are piles and haemorrhoids different?
Piles and haemorrhoids are actually the same medical condition, signifying enlarged veins in the lower rectum and anus. In normal cases, these veins act as cushions to the anus and regulate stool. When they get inflamed or swollen, they may produce some symptoms like pain, bleeding, etc.
- What is the ideal treatment for piles?
Several treatments are available for piles, including creams, ointments, suppositories, tablets, and fibre supplements. Home treatments such as increasing fibre intake and modifying lifestyle are also beneficial.
- When do you need to see a doctor for haemorrhoids?
You need to go see a doctor if you notice any of the following:
- Ongoing or heavy bleeding, with or without pain
- Pus from haemorrhoids
- High fever
- Extreme pain
Conclusion
Overall, haemorrhoids and piles are the same condition in which the veins in the anus or rectum become swollen. Understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment of piles can help you deal with this common condition effectively.
For aspiring medical students studying for the NEET PG exam, learning about haemorrhoids in detail is essential. In this regard, DocTutorials can serve as an ideal solution. With professional video courses, Quick Revision Programs (QRPs), and interactive tools, DocTutorials ensures you are all set to crack your exams and ready to face any medical challenges with confidence. Check out our NEET PG study materials today!
Latest Blogs
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…




