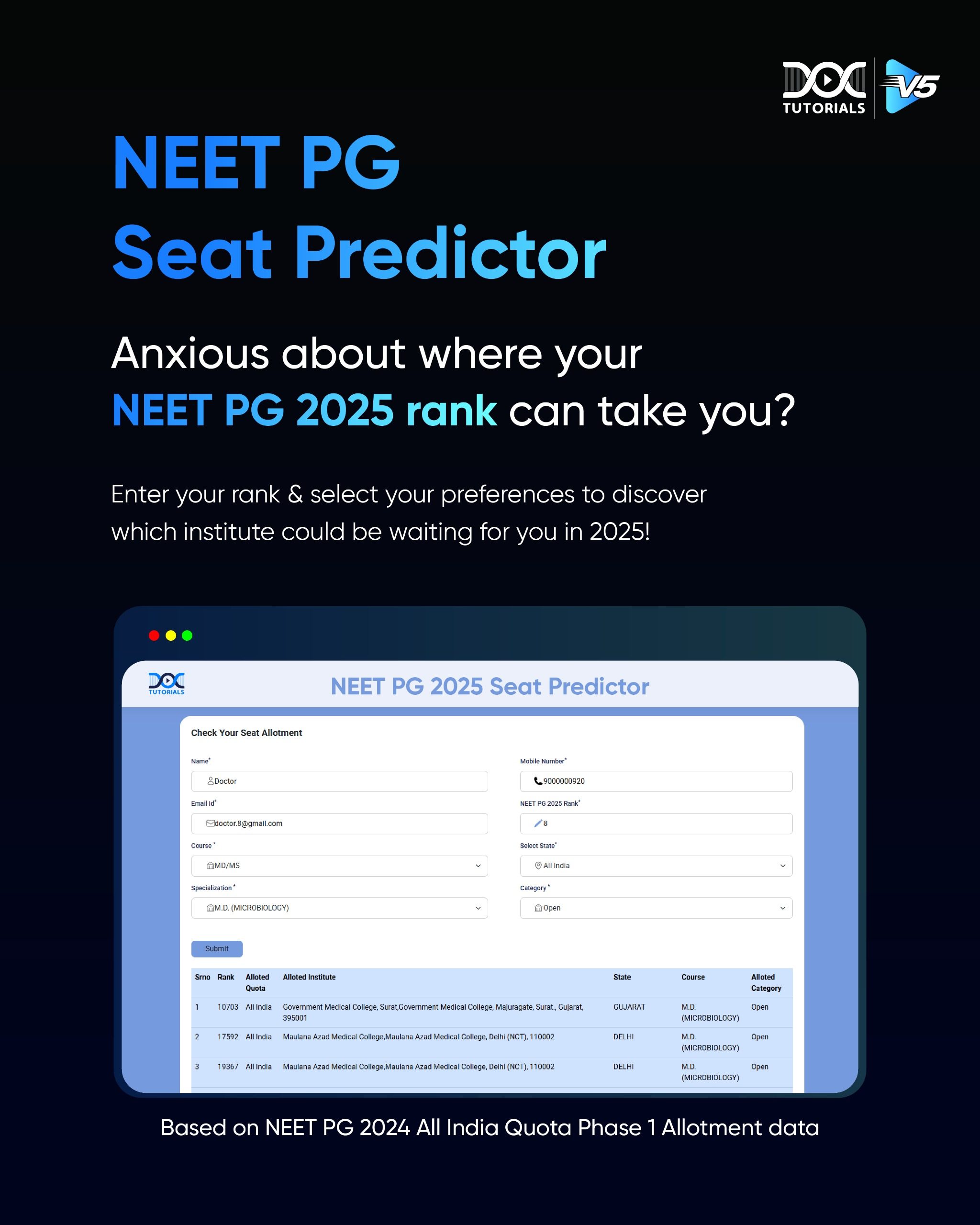
Bronchial Asthma | Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Treatment

Bronchial asthma is a respiratory disorder that affects the lungs. According to records, nearly 5% -10% of individuals of all age groups suffer from this lung disease. It has been a global health hazard, but can be managed with the right medicines and lifestyle.
If you’re preparing for the NEET PG exam, it is essential to understand the concept of bronchial asthma. Read on to learn more about its types, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis process, and treatment methods.
What is Bronchial Asthma?
Bronchial asthma, commonly known as asthma, is a chronic disease that causes inflammation of the airways. This inflammation leads to sensitive reactions to stimuli through contraction and constriction. The mucous membranes in the bronchial tubes swell, forming thick mucus.
The affected individual’s respiratory muscles cramp, causing acute respiratory distress. However, bronchial asthma is not “cardiac asthma,” which is characterised by fluid buildup in the lungs due to left ventricular weakening.
What are the Types of Bronchial Asthma?
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, the following are the 2 bronchial asthma types:
- Intermittent
Intermittent bronchial asthma often comes and goes. So, the affected individual can feel normal between the flares of asthma.
- Persistent
If you have persistent asthma, you experience symptoms most of the time. Mild, moderate, and severe symptoms are all possible. Medical professionals use the frequency of symptoms to determine the severity of asthma. They also consider your ability to perform tasks during an attack.
What are the Risk Factors of Bronchial Asthma?
Here are some of the common risk factors that can trigger the bronchial asthma condition:
- Irritants like air pollution, chemical fumes, smoke, strong odours, etc.
- Exercise or any other physical activity, especially if performed in dry or cold air
- Allergens like dust mites, pollen, pet dander, cockroaches and mould
- Flu, cold, or any other respiratory infections
- Extreme weather changes
- Smoking
- Certain drugs like beta-blockers, aspirin, NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), etc.
- MSG (monosodium glutamate) or other food additives
- Anxiety, emotional stress
- Crying, laughing, or singing
- Acid reflux
- Fragrances and perfumes, etc.
What are the Symptoms of Bronchial Asthma?
Bronchial asthma is a chronic condition where the airways become inflamed and overly sensitive, often reacting to allergens or irritants. When someone with asthma encounters a trigger, they may experience an asthma attack.
If symptoms begin within minutes, it’s called an immediate reaction. If they appear hours later, it’s a late reaction. The attack happens because the airways narrow due to swelling, excess mucus, and tightening of the surrounding muscles. This further makes it hard to breathe.
Here are some of the symptoms that one may experience during an asthma attack:
- A person might suddenly struggle to breathe
- Hear a whistling sound (wheezing) when exhaling
- Feel chest tightness
- Experience fear of suffocation
- Breathing and heart rates can increase
- A persistent cough with thick mucus may occur.
In severe cases, the lips and face may turn blue due to low oxygen. Attacks can last from seconds to hours, and if they persist for days, it’s called “status asthmaticus,” a medical emergency.
How to Diagnose Bronchial Asthma?
Asthma symptoms often don’t appear during a doctor’s visit. So, it’s crucial to describe your or your child’s symptoms and when they occur, especially during exercise, after exposure to smoke, or when having a cold.
To help diagnose and monitor asthma, doctors use the following tests:
- Spirometry
It is a lung function test where you breathe into a device called a spirometer to measure how much air you can inhale and exhale and how quickly.
- Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF)
It uses a peak flow meter to measure how forcefully you can exhale; this can be done at home to track asthma control over time.
- Chest X-ray
It is used to check for other illnesses that might cause similar symptoms. These tests and your symptom descriptions help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective asthma management plan.
What are the Treatment Options for Bronchial Asthma?
Bronchial asthma is managed through a mix of medications and lifestyle changes. The main goal is to control symptoms and prevent attacks. Medications include the following:
- Bronchodilators: They quickly open the airways during an asthma attack
- Corticosteroids (inhaling): They reduce inflammation in the lungs.
Doctors may prescribe oral corticosteroids for more severe cases to further decrease airway inflammation. Alongside medication, it’s important to avoid known triggers like allergens, smoke, or strong odours, as these can worsen symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as regular exercise and not smoking, also helps manage asthma. Although asthma cannot be cured, it can be kept under control with the right treatment plan.
Regular use of inhalers, taking prescribed oral medications when necessary, and staying alert to symptoms allow people with asthma to reduce the risk of severe attacks. Monitoring symptoms and avoiding triggers are key to effective asthma management.
FAQs About Bronchial Asthma
- How to prevent bronchial asthma?
Although asthma can’t be fully prevented, you can lower your risk and avoid attacks by avoiding allergens, practising good hygiene, getting vaccinated, staying fit, and eating well.
- Can individuals of any age get asthma?
Anyone can develop asthma at any age, but people with allergies or those exposed to tobacco smoke are at higher risk. Asthma is more common in females and affects Black individuals more frequently than other groups.
- Can bronchial asthma be life-threatening?
Although severe asthma attacks can be dangerous, most people manage asthma well with proper treatment. An asthma action plan and seeking quick medical help during attacks are essential.
- What are the long-term risks if bronchial asthma goes untreated?
Untreated asthma can cause permanent airway changes, reduced lung function, frequent infections, and more hospital visits. It may also lower the quality of life and make daily activities and exercise difficult to perform.
Conclusion
Bronchial asthma has no cure yet, but one can manage it by following the necessary lifestyle modifications, taking medicines, etc. Whether you are an asthma patient or not, knowing its symptoms, causes, and management can help you save lives.
Moreover, if you are a medical student preparing for NEET PG, you must learn about bronchial asthma, which is an essential topic of your syllabus. You can join DocTutorials if you are looking for a professional NEET PG course to ensure your success.
Our experienced faculty, advanced study materials, timely assessment, etc., are designed to assist you in the best way possible.
Join our NEET PG course to learn more!
Latest Blogs
-

NEET SS Exam 2024: Analysis, Key Dates, Counselling
The NEET SS 2024 exam kicked off on March 29, 2025. Over two days and two slots, candidates across 13…
-

NEET PG Registration 2025: An Essential Guide For Exam Prep
The NEET PG registration, which is conducted online, is a crucial step in the exam process. Filling out the NEET…
-

NEET PG Syllabus 2026: A Must-Have Complete Guide for Exam Success
The NEET PG Syllabus acts as one of the foundation stones for aspiring postgraduate medical students like you who are…