Candidiasis Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & More | NEET PG Guide

Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by Candida, most often Candida albicans. These fungi are commonly found in the environment and also naturally inhabit various parts of the body, including the mouth, digestive tract, and intimate areas.
Normally, the body’s friendly bacteria and immune system help keep these fungi under control. However, if this balance is disturbed-for example, by antibiotics or changes in the body’s moisture or pH levels-the yeast can grow excessively and even lead to infection.
Read more to know how this condition develops, candidiasis treatment, and who may be more vulnerable to it!
What is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis can generally affect different parts of the body, causing mild or more serious candida symptoms depending on a person’s overall health. Here is a detailed overview:
- In healthy people, it usually appears as oral thrush, skin rashes, or vaginal infections.
- Moist areas, such as the underarms or the groin, are common spots for skin infections. Vaginal yeast infections, also known as candida vaginitis, are very common and may happen more often during pregnancy or due to certain medications.
- In people with weakened immune systems, such as cancer patients or newborns, the infection can become severe, spreading into the bloodstream and affecting internal organs-a condition known as deep or invasive candidiasis.
What are the Causes and Risk Factors of Candidiasis?
Certain conditions and changes in the body can create an environment where candidiasis grows more than it should. Here are some common factors that can lead to this medical condition:
- Antibiotic Use: Some antibiotics reduce the healthy bacteria in the vagina, giving yeast a chance to grow.
- Hormonal Changes: Shifts in hormones due to pregnancy, birth control pills, or your monthly cycle can also affect natural balance.
- Weak Immunity: Health conditions or medications that lower your immune defences can even make you more prone to candidiasis infection.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes: High sugar levels in urine can feed yeast and raise the risk of infection.
Other Risk Factors of Candidiasis
Apart from internal changes, certain daily habits can also increase the chances of a yeast infection:
- Wearing damp clothes or swimwear for extended periods.
- Wearing tight or non-breathable fabrics that trap heat and moisture.
- Using scented feminine products such as soaps, sprays, or tampons that may irritate the vaginal area.
What are the Symptoms of Candidiasis?
Candida symptoms can usually appear in different ways. Here are the essential symptoms you should look out for:
- Red or discoloured rash that may be intensely itchy
- Cracked, sore, or broken skin in the affected area
- Blisters or small pus-filled spots in some cases
It usually appears in skin folds, such as:
- Underarms
- Groin area
- Between the fingers
- Under the breasts
Candidiasis symptoms can also affect:
- Nails or the skin around the nails
- Inside the mouth (thrush)
- Corners of the lips
Other skin issues like psoriasis, eczema, ringworm, or dermatitis can look similar, so it’s best to get a proper check-up if symptoms appear.
How is Candidiasis Diagnosed?
Your doctor may suspect the infection based on the symptoms you describe. To be sure, they might take a small sample of vaginal discharge for testing. The doctor can confirm if it’s a candidiasis infection and decide on the right treatment for you by looking at both your symptoms and the test results.
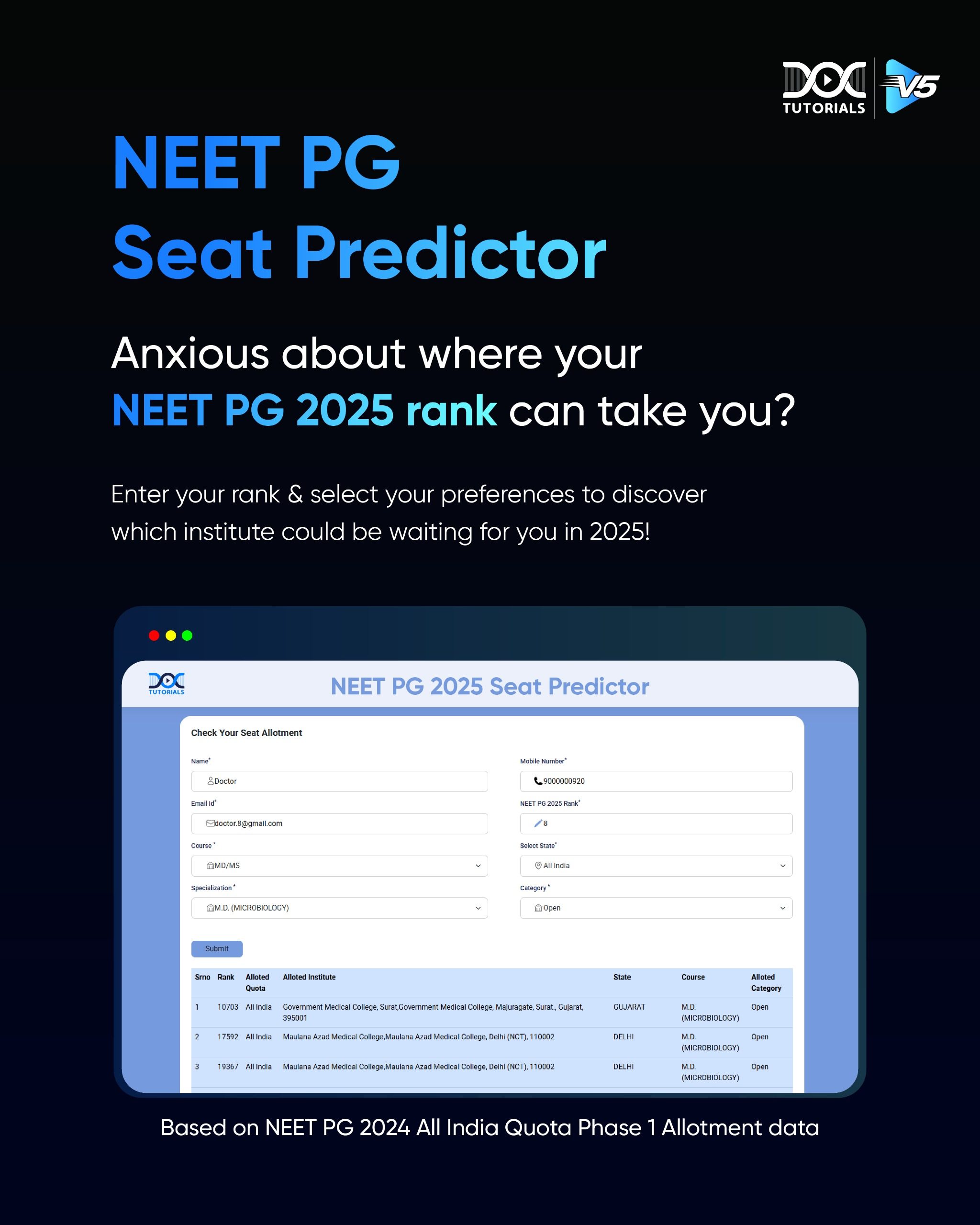
How is Candidiasis Treated?
The candidiasis treatment generally depends on which part of the body is affected, such as:
- Thrush (mouth): Mild cases are treated with antifungal mouthwashes or lozenges. More serious cases may need tablets like fluconazole.
- Oesophagitis (throat): Treated with oral antifungal medicine, usually fluconazole.
- Skin Infections: Antifungal creams or powders work well. Make sure the area stays clean, dry, and protected from rubbing or irritation.
- Vaginal Infections: Treated with antifungal tablets, creams, or suppositories placed in the vagina. Just one dose of fluconazole can sometimes be effective.
- Deep Infections: Serious cases need antifungal medicines given through a drip, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
How to Prevent Candidiasis?
While candida vaginitis is common, you can often avoid it by following a few simple habits in your daily routine. Making these small adjustments can support your body’s natural balance and even lower the chances of getting an infection:
- Avoid douching, as it can wash away the helpful bacteria that protect against fungal overgrowth.
- Stay away from vaginal sprays or perfumed products, which may irritate the area.
- Avoid using fragranced pads or tampons, as the added scents may disturb your body’s natural balance.
- Change out of wet clothes quickly, especially after swimming or exercising, to keep the area dry.
- Wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing to allow better airflow and reduce moisture build-up.
- If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar well managed, since high levels can encourage the growth of candidiasis infection.
FAQs About Candidiasis
- What does cutaneous candidiasis look like?
The appearance of a candida skin infection changes depending on the area affected:
- Diaper Area: Red or patchy rash, sometimes with small bumps, often itchy or burning.
- Skin Folds: Moist, red rash with possible bumps and itching.
- Vagina: White or yellow discharge, redness, and itching, especially when passing urine.
- Mouth (thrush): White or red patches inside the cheeks and tongue, with pain or difficulty swallowing.
- Corners of the Mouth: Sore, red splits, or tiny cuts that can be painful.
- Nail Folds: Thickened, discoloured nails with swelling or pain around the nails.
- How do you get rid of candidiasis quickly?
The time of treatment generally depends on the severity of the infection. Antifungal creams like clotrimazole can improve symptoms in a few days, but treatment may last up to four weeks. Always continue using the cream for two weeks after candidiasis symptoms stop to prevent the infection from returning.
- What is the best treatment for candidiasis?
Candidiasis treatment mainly depends on its type and infection severity. Common antifungal creams include:
- Clotrimazole
- Nystatin
- Miconazole
- Is a candida infection contagious?
Candida infection is usually not contagious. Rarely, a female partner might catch it, but it’s uncommon to pass it to a male partner.
- Is yeast infection dangerous?
Usually, yeast infections are not dangerous but can cause discomfort. In rare cases, they may lead to complications if left untreated.
- Is candida a sexually transmitted disease?
Candida infection is generally not classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD), although transmission to female partners is rare.
- Can I use over-the-counter treatments for candidiasis?
You may be able to relieve candidiasis symptoms with over-the-counter medicines. But if you’re not certain about the cause, it’s wise to consult a healthcare expert for proper treatment.
- How long does candidiasis last?
Most cases improve within a few days of candidiasis treatment, though some may take up to a week. More serious infections could need extra time to heal. Make sure to complete the full course of medication to prevent the infection from coming back.
Conclusion
Candidiasis is a very common fungal issue that many women experience at some point in their lives. They are easily treated with medicines, many of which can be bought over the counter at your local pharmacy.
Even if a person is familiar with candidiasis symptoms, it’s still important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and care. They can identify the exact type of infection and suggest the most effective treatment based on its severity.
Understanding candidiasis is important for overall health. DocTutorials offers excellent study materials, high-quality video lessons, and quick revision programs to help you learn more about candidiasis, how it develops, and several ways to manage it effectively.
Want to improve your knowledge base and ace your medical exams? Enrol in our NEET PG courses today!
Latest Blogs
-
-

NEET SS Exam 2024: Analysis, Key Dates, Counselling
The NEET SS 2024 exam kicked off on March 29, 2025. Over two days and two slots, candidates across 13…
-

NEET PG Registration 2025: An Essential Guide For Exam Prep
The NEET PG registration, which is conducted online, is a crucial step in the exam process. Filling out the NEET…