NEET PG 2025 PYQs: Subject-Wise Recall Questions & Answers

Preparing for NEET PG isn’t just about mastering concepts. It’s also about understanding the exam pattern and recognizing frequently asked topics. One of the smartest strategies to boost your preparation is practicing Previous Year Questions (PYQs).
In this article, we bring you a complete subject-wise collection of NEET PG PYQs with detailed answers, designed to support aspirants at every stage of their journey.
Here’s how this resource can help you:
- Gain clarity on the exam pattern and recurring question trends
- Pinpoint high-yield topics across each subject
- Get comfortable with a real exam-like format
- Sharpen your speed, accuracy, and confidence
- Strengthen weaker areas with focused subject-wise practice
Whether you’re in the early stages of preparation or revising closer to the exam, these NEET PG 2025 PYQs with solutions will give you an extra edge and help maximize your performance on exam day.
NEET PG 2024 Previous Year Question Paper with Solutions Session 1 & Session 2
Here’s the NEET PG 2024 Previous Year Question Paper with detailed solutions – everything you need to boost your NEET PG preparation!
| NEET PG 2024 Previous Year Question Paper Session 1 Pdf | NEET PG 2024 Previous Year Question Paper Session 2 Pdf |
NEET PG 2025 Anatomy Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Non-clinical question
1. Which of the following nerves does not pass through the marked structure?
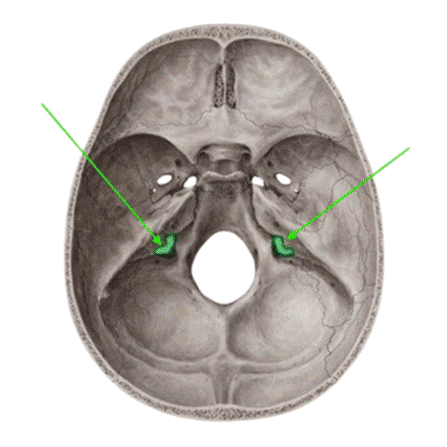
Options:
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Vagus nerve
- Spinal accessory nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
Correct Answer: D) Hypoglossal nerve
Question 2
Non-clinical question
The persistence of which of the following arch arteries is responsible for the congenital anomaly marked in the image given below?
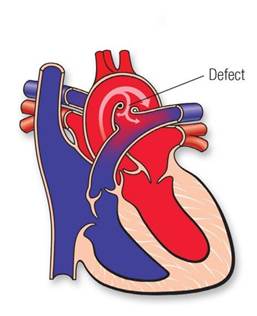
Options:
- 6th left pharyngeal arch artery
- 6th right pharyngeal arch artery
- 4th left pharyngeal arch artery
- 4th right pharyngeal arch artery
Correct Answer: A) 6th left pharyngeal arch artery
Question 3
Non-clinical question
Upon the delivery of a term new born, a thorough examination of the umbilical cord reveals crucial information. What are the essential components of a healthy umbilical cord?
Options:
- 2 arteries and 1 vein
- 2 veins and 1 artery
- 1 vein and 1 artery
- 2 veins and 2 arteries
Correct Answer: A) 2 arteries and 1 vein
Question 4
clinical question
A woman presented with complaints of loss of sensation over the lateral aspect of the thigh and was diagnosed with meralgia paresthetica. The nerve involved in this condition arises from which of the following nerve roots?
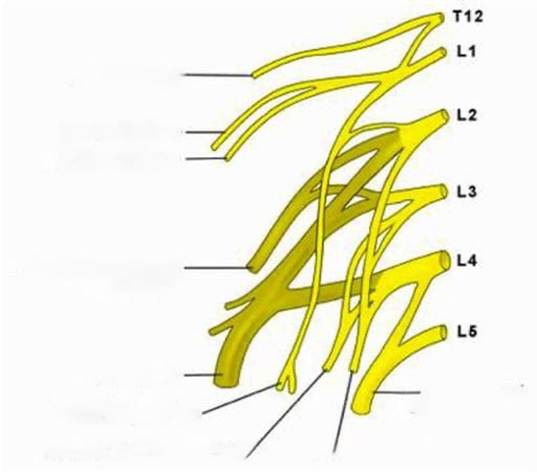
Options:
- T12 and L1
- L1 and L2
- L2 and L3
- L2, L3, and L4
Correct Answer: C) L2 and L3
Question 5
Non-clinical question
The epithelium depicted in the image below is seen in which of the following structures?
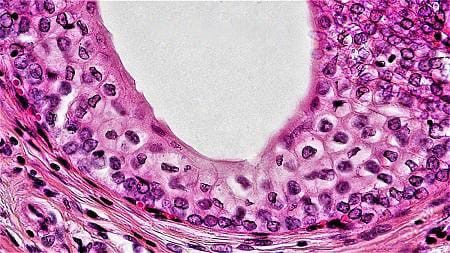
Options:
- Esophagus
- Ureter
- Trachea
- Duodenum
Correct Answer: B) Ureter
Question 6
Non-clinical question
A 19-year-old boy presented to the OPD with shoulder pain. He had been training in the gym and had hyperextended his shoulder. On examination, the avulsion of the long head of the triceps was noticed. What is the site at which avulsion of the long head of triceps occurs?
Options:
- Shaft of the humerus
- Delotoid tuberosity of the humerus
- Infraglenoid tubercle
- Supraglenoid tubercle
Correct Answer: C) Infraglenoid tubercle
Question 7
Non-clinical question
Identify the marked structure
Options:
- Thyroid cartilage
- Epiglottis
- Pyriform sinus
- Valllecula
Correct Answer: C) Pyriform sinus
Question 8
Non-clinical question
A 75-year-old male who is a known case of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with epistaxis, which does not respond to conservative measures and nasal packing. Which of the following arteries should be prioritised for ligation?
Options:
- Posterior ethmoidal artery
- Anterior ethmoidal artery
- Sphenopalatine artery
- Greater palatine artery
Correct Answer: C) Sphenopalatine artery
Question 9
Non-clinical question
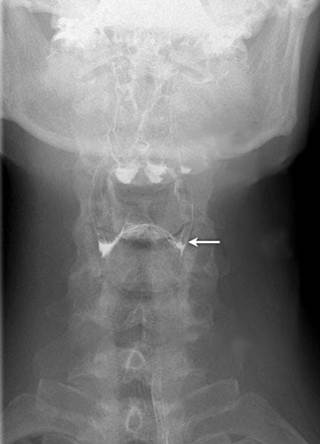
The marked structure does not have which of the following components?
Options:
- GVE
- GVA
- GSA
- GSE
Correct Answer: D) GSE
Question 10
Non-clinical question
Which pair of nerves supplies the muscles marked A and B, respectively?
Options:
- Nerve to the mylohyoid and the facial nerve
- Facial nerve and spinal accessory nerve
- Spinal accessory nerve and facial nerve
- Ansa cervicalis and hypoglossal nerve
Question 11
Non-clinical question
During eversion of the foot, which of the following ligaments is most likely to be injured?
Options:
- Anterior talofibular
- Deltoid ligament
- Posterior talofibular
- Calcaneofibular
Correct Answer: B) Deltoid ligament
Question 12
Clinical question
During an abdominal surgery, the surgeon accidentally nicks a structure that passes posterior to the epiploic foramen, which results in profuse bleeding. Which of the following structures is most likely to get injured?
Options:
- Aorta
- Hepatic artery
- IVC
- Portal vein
Correct Answer: C) IVC
Question 13
Non-clinical question
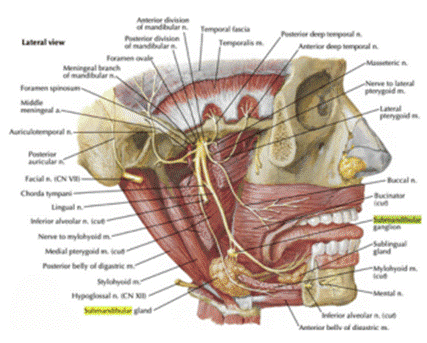
Identify the marked structure that passes inferior to the posterior belly of the digastric and can be seen after submandibular gland resection.
Options:
- Facial artery
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Marginal mandibular nerve
- Facial nerve
Correct Answer: B) Hypoglossal nerve
Question 14
Non-clinical question
A patient presents with cancer near the anal opening. Which of the following groups of lymph nodes is most likely to be involved in this patient?
Options:
- Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
- Deep inguinal lymph nodes
- Internal iliac lymph nodes
- External iliac lymph nodes
Correct Answer: A) Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
Question 15
Non-clinical question
A patient presents with muscle wasting, reduced tone, and weakness of the right hand. Fine motor movements, such as dough kneading, are also affected. Which of the following structures is most likely to be impaired in this patient?
Options:
- Anterior grey horn of the spinal cord in the cervical region
- Internal capsule
- Corticospinal tract in the cervical region
- Brainstem
Correct Answer: A) Anterior grey horn of the spinal cord in the cervical region
NEET PG 2025 Anaesthesia Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical question
Following administration of a muscle relaxant, the patient develops erythema, flushing, and a drop in blood pressure. Which of the following agents is most likely responsible?
Options:
A) Vecuronium
B) Atracurium
C) Cis-atracurium
D) Pancuronium
Correct answer: B) Atracurium
Question 2
Clinical question
A 35-year-old male undergoing abdominal surgery under general anaesthesia develops
sudden generalised muscle rigidity, rapid increase in body temperature, and tachycardia shortly
after administration of sevoflurane and succinylcholine. His end-tidal CO₂ is rising despite
controlled ventilation. What is the most appropriate immediate treatment?
Options:
A) Dantrolene
B) Paracetamol
C) Calcium chloride
D) Propranolol
Correct answer: A) Dantrolene
NEET PG 2025 Biochemistry Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical question
A labourer was stuck in a tunnel for 5 days without food. Which of the following processes serves as the primary source of energy for the brain during this time?
Options:
A) Glycogenolysis
B) Gluconeogenesis
C) Ketogenesis
D) Lipolysis
Correct answer: C) Ketogenesis
Question 2
Clinical question
Under an experimental condition, blood glucose level is spiked to 2-3 times the normal level and is sustained at this level. Which of the following describes the pattern of insulin levels in the blood?
Options:
A) Sudden rise in insulin followed by a slower, sustained drop in insulin
B) Continuous increase in insulin until a maximum concentration
C) Increase in insulin followed by a decrease below the baseline level
D) Sudden initial increase followed by a delayed but higher and continuing increase in insulin levels
Correct answer: D) Sudden initial increase followed by a delayed but higher and continuing increase in insulin levels
Question 3
Non-clinical question
A patient presents with ataxia, anaemia, and sensory neuropathy. Laboratory tests show elevated total homocysteine and methylmalonic acid levels. Production of which of the following amino acids could be affected?
Options:
A) Tyrosine
B) Glutamine
C) Cysteine
D) Methionine
Correct answer: D) Methionine
Question 4
Clinical question
A patient on long-term hydrochlorothiazide presents with features of heart failure,
horizontal nystagmus, and peripheral neuropathy. There is no history of alcohol use or smoking. Which of the following deficiencies can cause this presentation?
Options:
A) Thiamine
B) Selenium
C) Zinc
D) Vitamin B12
Correct answer: A) Thiamine
Question 5
Clinical question
A 10-year-old boy presents with coarse facial features, organomegaly, corneal opacity, and peripheral neuropathy. A deficiency of the enzyme alpha-L-iduronidase is found. Which of the following is accumulated in this condition?
Options:
A) Dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate
B) Dermatan sulfate
C) Keratan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate
D) Sphingolipids
Correct answer: A) Dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate
Question 6
Clinical question
A 10-year-old presents with multiple freckles and hyperpigmentation that worsens with sun exposure. Examination reveals two basal cell carcinomas on the face. Which of the following DNA repair mechanisms is defective?
Options:
A) Base excision repair
B) Nucleotide excision repair
C) DNA mismatch repair
D) DNA double-strand break repair
Correct answer: B) Nucleotide excision repair
Question 7
Clinical question
A 10-month-old boy presents with recurrent oral lesions and respiratory infections. Laboratory investigations reveal reduced B cell, T cell, and NK cell counts along with reduced adenosine
deaminase levels. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Agammaglobulinemia
B) Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
C) DiGeorge syndrome
D) Severe combined immunodeficiency
Correct answer: D) Severe combined immunodeficiency
Question 8
Non-clinical question
Which of the following molecular diagnostic tests is useful in syndromic conditions like meningitis?
Options:
A) Uniplex PCR
B) Multiplex PCR
C) Nested PCR
D) Arbitrarily primed PCR
Correct answer: B) Multiplex PCR
Question 9
Non-clinical question
A frameshift mutation was introduced into the coding sequence of an mRNA. If this occurs at the 4th position in an mRNA with 900 nucleotides, which of the following is most likely to happen?
Options:
A) No biological change
B) Partial loss of protein and function
C) Complete loss of protein and function
D) No change in function as it will be removed in post-translational modification
Correct answer: C) Complete loss of protein and function
Question 10
Clinical question
A 40-year-old woman who underwent ileal resection presents with features of anaemia despite a balanced diet. Her RBC count is 2.8 million/mm³, and serum iron is 164 mcg/dL. Which of the
following is most likely to be found in her?
Options:
A) Iron deficiency anaemia
B) Megaloblastic anaemia
C) Aplastic anaemia
D) Hemolytic anaemia
Correct answer: Megaloblastic anaemia
Question 11
Non-clinical question
Which of the following, if given in large volumes, can lead to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis?
Options:
A) Dextrose in NS (DNS)
B) Normal saline
C) 5% dextrose in water
D) Ringer’s lactate
Correct answer: B) Normal saline
Question 12
Clinical question
A patient presents with bleeding symptoms and factor 9 deficiency that resolve after
administration of a vitamin K injection. Which of the following is the most likely underlying condition?
Options:
A) Classical haemophilia
B) Biliary obstruction
C) Pernicious anaemia
D) Hepatitis A
Correct answer: B) Biliary obstruction
Question 13
Clinical question
A child presents with elevated concentrations of phenylalanine. Phenylalanine hydroxylase activity is found to be normal. Which of the following coenzymes, also required for tyrosine metabolism, could be deficient in this child?
Options:
A) Biopterin
B) Pyridoxal phosphate
C) Adenosylcobalamin
D) Dihydrofolic acid
Correct answer: A) Biopterin
Question 14
Clinical question:
An 8-year-old boy presents to the OPD for evaluation of a subcutaneous xanthoma on his right elbow. His father recently died of a myocardial infarction, and there is a family history of similar findings. Laboratory investigations reveal total cholesterol of 480 mg/dL, triglycerides of 146 mg/dL, and LDL cholesterol of 300 mg/dL. Which of the following types of
Familial hyperlipoproteinemias is the most likely underlying condition?
Options:
A) Type I
B) Type IIa
C) Type IIb
D) Type III
Correct answer: B) Type IIb
Question 15
Clinical Question:
A 70-year-old man presents with a fracture following trivial trauma. He also has perifollicular haemorrhages, lusterless hair, and dry skin. He is on an exclusive diet of toast and buns and has microcytic hypochromic anaemia. Which of the following enzymes is most likely affected in this patient?
Options:
A) Prolyl hydroxylase
B) ALA synthase
C) Glutathione peroxidase
D) Dihydrofolate reductase
Correct answer: A) Prolyl hydroxylase
Question 16
Clinical question:
A 7-month-old infant presents with developmental delay, seizures, and a cherry-red spot on fundoscopy. The mother has a history of an abortion at 8 weeks. Genetic testing reveals a deficiency of hexosaminidase A. Which of the following accumulates in this condition?
Options:
A) GM1 ganglioside
B) GM2 ganglioside
C) Galactocerebroside
D) Sphingolipids
Correct answer: B) GM2 ganglioside
Question 17
Clinical question:
A boy presents with orange-colored tonsils and a family history of multiple cardiovascular-related deaths. Laboratory investigations show total cholesterol of 80 mg/dL, triglycerides 146 mg/dL, HDL <5 mg/dL, and LDL 90 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Niemann-Pick disease type C
B) Tangier disease
C) Familial abetalipoproteinemia
D) Familial hyperlipoproteinemia type I
Correct answer: B) Tangier disease
NEET PG 2025 Dermatology Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical Question
A 20-year-old presented with a non-progressive hypopigmented skin lesion that has been present since birth. It shows white accentuation under Wood’s lamp examination, and diascopy is inconclusive. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Vitiligo
B) Nevus depigmentosus
C) Nevus anaemicus
D) Indeterminate leprosy
Correct Answer: B) Nevus depigmentosus
Question 2
Non-Clinical Question
An image shows the characteristic skin findings of phrynoderma, described as plugged keratotic papules. Which of the following should be done next?
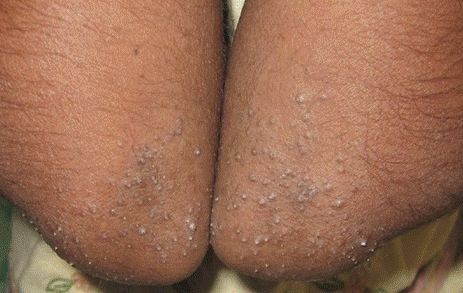
Options:
A) Ocular examination
B) Vitamin D3 status
C) Deep tendon reflexes
D) Vitamin B12 status
Correct Answer: A) Ocular examination
Question 3
Clinical Question
A patient presents with a plaque on the face with central clearing and atrophy, and his chest X-ray demonstrates apical calcification. Which of the following can be used for the diagnosis of the underlying condition?
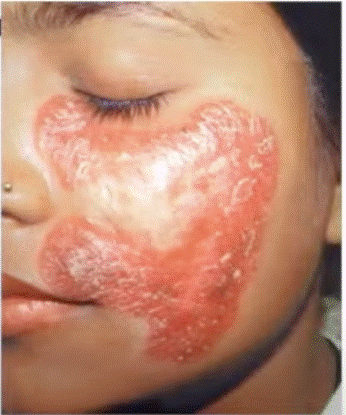
Options:
A) PCR
B) Mantoux test
C) Slit skin smear test
D) Probe test
Correct Answer: A) PCR
NEET PG 2025 ENT Previous Year Questions
Q.1
Clinical Question:
A 28-year-old male with a history of chronic ear discharge and hearing loss undergoes an otoscopic evaluation. The image below shows a large central perforation of the tympanic membrane with visible middle ear structures. What is the most appropriate surgical intervention for this patient?
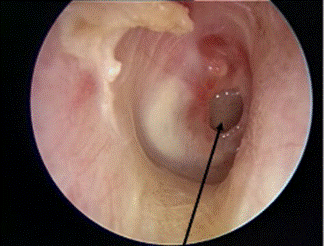
Options:
- Atticotomy
- Modified radical mastoidectomy
- Myringoplasty
- Tympanoplasty
Correct Answer: D) Tympanoplasty
Q.2
Clinical Question:
An industrial worker presents with hearing loss. On examination, Rinne’s test was negative on the left side and positive on the right side. Weber’s test lateralized to the left side. Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA) was done with the results as shown below. What is the most appropriate diagnosis?
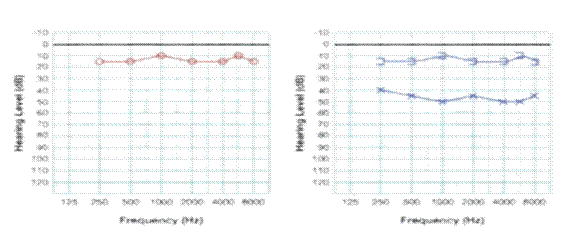
Options:
- Right conductive hearing loss
- Left conductive hearing loss
- Right sensorineural hearing loss
- Left sensorineural hearing loss
Correct Answer: B) Left conductive hearing loss
Q.3
Clinical Question:
A 12-year-old male presents with recurrent, profuse nasal bleeding and right-sided nasal obstruction. Endoscopy reveals a globular, vascular mass in the right nasal cavity occupying the posterior choanae and nasopharynx. A CT scan shows anterior bowing of the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. What is the most likely diagnosis?
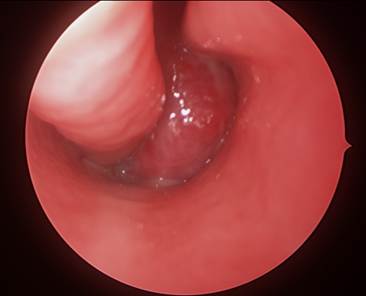
Options:
- Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
- Antrochoanal polyp
- Rhinoscleroma
- Rhinosporidiosis
Correct Answer: A) Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Q.4
Clinical Question:
A patient presents to the emergency department with significant nasal trauma after a fall.
Examination reveals a deviated nasal pyramid, and palpation confirms crepitus and mobility of
the nasal bones. A lateral nasal bone X-ray confirms a displaced nasal bone fracture. Which of
the following instruments is specifically designed for the closed reduction of a displaced nasal
bone fracture?
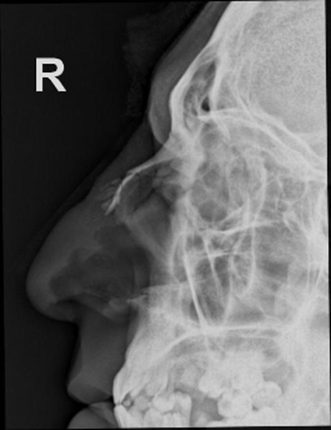
Options:
- Tilley’s forceps
- Luc’s forceps
- Walsham forceps
- Bayonet forceps
Correct Answer: C) Walsham forceps
Q.5
Clinical Question:
Following a building collapse, a male patient was brought to the emergency department with a copious amount of debris in the mouth, making endotracheal intubation impossible. The emergency procedure shown in the image was performed. Which of the following statements regarding this procedure is true?
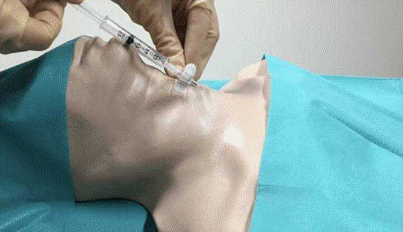
Options:
- It is used for effective ventilation for up to 6 hours
- It is used to measure central venous pressure
- It should be followed by a tracheostomy
- The work of breathing is more than with bag-and-mask ventilation
Correct Answer: C) It should be followed by a tracheostomy
Q.6
Clinical Question:
A 3-year-old child presents to the casualty in an unresponsive state after consuming peanuts. What is the most appropriate immediate management?
Options:
- Give abdominal thrusts
- Give 5 back slaps
- Start chest compressions
- Attempt endotracheal intubation
Correct Answer: C) Start chest compressions
Q.7
Clinical Question:
A 72-year-old female smoker presents with a long history of hoarseness of voice, difficulty swallowing, and difficulty breathing. The patient was diagnosed with laryngeal cancer and underwent surgical management. The post-operative picture is shown below. Which of the following surgeries was most likely performed on the patient?
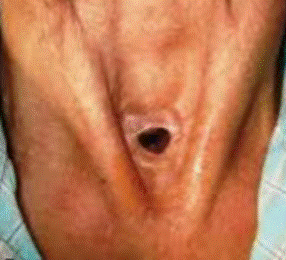
Options:
- Partial laryngectomy
- Total laryngectomy
- Standard tracheostomy
- Percutaneous tracheostomy
Correct Answer: B) Total laryngectomy
Forensic Medicine
NEET PG 2025 Forensic Medicine Previous Year Questions
Question: 1
Clinical question
A 26-year-old woman is brought dead to the emergency department. On examination, there are multiple crescentic abrasions over the sides of her neck and lower jaw, along with deep bruising of neck muscles on internal dissection during autopsy. The hyoid bone is intact, but a minor haemorrhage is seen in the strap muscles. Which of the following is the most likely cause of death?
Options:
- Ligature Strangulation
- Mugging
- Throttling
- Garroting
Correct Answer: C) Throttling
Question 2
Non-clinical question
As per the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, who is legally considered a child under the law for protection against sexual offences?
Options:
- Girls under 16 years of age
- All children under 16 years of age
- All children under 18 years of age
- Girls under 18 years of age
Correct Answer: C) All children under 18 years of age
Question 3
Non-clinical question:
Which of the following statements regarding the “Zasko phenomenon” is true?
Options:
A) It refers to the postmortem clotting of blood
B) It is used to describe the gaping of a wound along skin tension lines
C) It refers to the tendon reflex after death
D) It is used to describe the seeping of blood from wounds at the time of death
Correct Answer: C) It refers to the tendon reflex after death
Question 4
Non-clinical question
A 22-year-old male is found dead in his room. On autopsy, the stomach contents emit a strong garlic-like odour, and red-velvet discolouration of the gastric mucosa is noted, along with greyish granular material resembling pesticide powder. Which of the following is the most likely poison involved?
Options:
A) Organophosphorus compound
B) Acute arsenic poisoning
C) Aluminium phosphide
D) Carbamates
Correct Answer: B) Acute arsenic poisoning
Question 5
Clinical question
A 16-year-old girl and a 23-year-old boy undergo medical examination following allegations of rape made by the girl’s parents. The girl states the sexual act was consensual, and no injuries were found on examination. According to the law, what is the legal status of the consent in this case?
Options:
- Consent is invalid as the girl is under 18 years old
- No punishment since the act was consensual
- No punishment since the man says he loves her and wants to marry her
- Parents must prove that the act was non-consensual
Correct Answer: A) Consent is invalid as the girl is under 18 years old
NEET PG 2025 Medicine Previous Year Questions
Question 1:
A patient presents with complaints of salt craving, generalized hyperpigmentation, and laboratory findings of hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Addison’s disease
B) Conn’s disease
C) Pheochromocytoma
D) Cushing’s syndrome
Correct Answer:
A) Addison’s disease
Question 2:
A critically ill patient with COVID-19 is admitted to the ICU and requires mechanical ventilation. The patient’s PaO₂/FiO₂ ratio is 100, consistent with severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Which of the following ventilatory strategies is most appropriate for managing this patient?
Options:
A) High PEEP and high tidal volume
B) Low PEEP and low tidal volume
C) Low PEEP and high tidal volume
D) High PEEP and low tidal volume
Correct Answer:
D) High PEEP and low tidal volume
Question 3:
A 15-year-old boy presents with progressive enlargement of hands and feet, coarse facial features, prominent enlarged jaw, and frontal bossing. On examination, he is noted to have bitemporal hemianopia. Which of the following is the most definitive test to confirm the diagnosis?
Options:
A) Increased IGF-1 levels
B) Decreased IGF-1 levels
C) Suppressed GH on administration of glucose
D) Non-suppressed GH on administration of glucose
Correct Answer: D) Non-suppressed GH on administration of glucose
Question 4:
A 69-year-old man presents with severe dyspnea and increasing amounts of clear sputum. ABG reveals pH 7.2, PCO₂ 66 mmHg, PaO₂ 44 mmHg, and bicarbonate 26 mEq/L. His SpO₂ is 77%. Which of the following is the underlying abnormality?
Options:
A) Metabolic acidosis
B) Metabolic alkalosis
C) Respiratory acidosis
D) Respiratory alkalosis
Correct Answer:
C) Respiratory acidosis
Question 5:
An asthmatic patient on salbutamol and ipratropium continues to have nocturnal exacerbations. Which of the following is the next best step?
Options:
A) Add oral corticosteroids
B) Switch to an inhaled corticosteroid plus a long-acting β2-agonist
C) Increase frequency of salbutamol
D) Add montelukast at night
Correct Answer: B) Switch to an inhaled corticosteroid plus a long-acting β2-agonist
Question 6:
A 19-year-old boy was diagnosed with meningococcal meningitis. What is the drug of choice (DOC) for prophylaxis to be given to his contacts?
Options:
A) Rifampicin
B) Ethambutol
C) Doxycycline
D) Amoxicillin
Correct Answer:
A) Rifampicin
Question 7:
A patient presents with pain and swelling of the knee joint. Synovial fluid aspirate shows rhomboid-shaped crystals that are positively birefringent under polarized light microscopy. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Gout
B) Pseudogout
C) Amyloidosis
D) Rheumatoid arthritis
Correct Answer:
B) Pseudogout
Question 8:
A patient presents with progressive skin thickening. Laboratory evaluation reveals ANA positivity along with anti–Scl-70 antibodies. Which clinical manifestation is most strongly associated with this antibody?
Options:
A) Gastric antral vascular ectasia
B) Calcinosis cutis
C) Interstitial lung disease
D) Raynaud’s phenomenon
Correct Answer: C) Interstitial lung disease
Question 9:
A patient presents with frothy sputum, hemoptysis, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and dyspnea on exertion. Lung biopsy reveals hemosiderin-laden macrophages. Which of the following conditions is least likely to be associated with this finding?
Options:
A) Volume overload
B) Right ventricular failure
C) Pulmonary vein obstruction
D) Protein-losing enteropathy
Correct Answer:
B) Right ventricular failure
Question 10:
A 50-year-old man presents to the emergency department with altered sensorium, hypotension, and shortness of breath. His arterial blood gas reveals a pH of 7.2, PaCO₂ of 44 mmHg, PaO₂ of 54 mmHg, HCO₃⁻ of 16 mEq/L, and a base excess of -12. Serum electrolytes show sodium 130 mEq/L and chloride 84 mEq/L. Based on these findings, what is the most likely acid–base disturbance?
Options:
A) Metabolic acidosis with anion gap of 30
B) Metabolic acidosis with anion gap of 20
C) Respiratory acidosis with anion gap of 30
D) Respiratory alkalosis with anion gap of 20
Correct Answer: A) Metabolic acidosis with anion gap 30
Question 11:
A 45-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, palpitations, and breathlessness. On examination, blood pressure and oxygen saturation are normal, jugular venous pressure is elevated, the pulse is irregular, and tender hepatomegaly is present. Cardiac examination reveals a heaving apex and a mid-diastolic murmur at the apex. She has a past history of acute rheumatic fever. Which of the following statements regarding this patient is false?
Options:
A) This patient has an increased risk of stroke
B) “a” wave is absent on JVP
C) This patient has features of right heart failure
D) Pre-systolic accentuation of the mid-diastolic murmur is a hallmark feature
Correct Answer: D) Pre-systolic accentuation of the mid-diastolic murmur is a hallmark feature
Question 12:
A patient presents with morning stiffness and tests positive for anti-CCP antibodies. Which of the following histological features is most characteristic of the underlying disease?
Options:
A) Synovial inflammation with pannus formation
B) Cartilage degeneration with osteophyte formation
C) Subepidermal blister with IgA deposits
D) Tophus with monosodium urate crystals
Correct Answer: A) Synovial inflammation with pannus formation
Question 13:
A 70-year-old patient with hypertension and atrial fibrillation presents with an acute-onset weakness of right side of body and aphasia, which began 2 hours ago. A non-contrast CT scan of the brain shows no evidence of haemorrhage. What is the next best step in management?
Options:
A) Administration of intravenous rTPA
B) Carotid Doppler ultrasound
C) Transesophageal echo
D) IV low molecular weight heparin
Correct Answer:
A) Administration of intravenous rTPA
Question 14:
An HIV-positive patient presents with a 2-week history of fever, cough, and weight loss. He is diagnosed with tuberculosis. What is the most appropriate approach to management?
Options:
A) Start antiretroviral therapy (ART) 2 weeks after initiating anti-tubercular therapy (ATT)
B) Start ATT and ART simultaneously
C) Start ART after completing the course of ATT
D) Start ATT 2 weeks after initiating ART
Correct Answer:
A) Start antiretroviral therapy (ART) 2 weeks after initiating anti-tubercular therapy (ATT)
Question 15:
A 55-year-old man with a long-standing history of diabetes mellitus presents with numbness and tingling in both feet. On examination, deep tendon reflexes in the lower limbs are reduced. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Options:
A) Bilateral distal symmetric polyneuropathy
B) Autonomic neuropathy
C) Mononeuropathy
D) Acute motor axonal neuropathy
Correct Answer: A) Bilateral distal symmetric polyneuropathy
Question 16:
A 21-year-old female, a known case of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), presents to the emergency department with altered sensorium. She has a history of missing her insulin doses for the past two days. On examination, her blood pressure is 80/60 mmHg and pulse rate is 103/min. Laboratory values reveal a serum sodium of 126 mEq/L, potassium 4.3 mEq/L, BUN 79 mg/dL, creatinine 2.2 mg/dL, and a random blood glucose level of 720 mg/dL. Which of the following is not a part of the initial management of this patient?
Options:
A) 3% NaCl
B) 0.9% NaCl
C) IV insulin
D) Monitor potassium level
Correct Answer:
A) 3% NaCl
Question 17:
A 55-year-old female presents with respiratory distress and hemoptysis on day 7 after knee replacement surgery. Her respiratory rate is 28/min, and pulse is 120/min. What is the most appropriate investigation?
Options:
A) Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan
B) Chest X-ray
C) CT Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA)
D) D-dimer
Correct Answer:
C) CT Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA)
Question 18:
A patient in altered sensorium is found to have a serum sodium of 95 mEq/L. She was treated with 3% hypertonic saline, and after 24 hours, her sodium level increased to 111 mEq/L. After sodium correction, her neurological status has deteriorated. What is the next best step in management?
Options:
A) Brainstem evoked potential
B) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
C) MRI brain
D) CSF analysis
Correct Answer:
C) MRI brain
Question 19:
A 12-year-old child with chronic kidney disease is admitted for evaluation of bone pain and growth retardation. Laboratory investigations reveal: serum calcium 7.2 mg/dL, serum phosphate 6.3 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 370 U/L, and elevated parathyroid hormone levels. X-ray of the long bones shows metaphyseal dysplasia. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Options:
A) Phosphate binders only
B) Oral calcium supplements
C) Calcium supplements with phosphate binders
D) Oral calcium with vitamin D
Correct Answer: C) Calcium supplements with phosphate binders
Question 20:
A 70-year-old male presents to the emergency department with dyspnea and palpitations for the past 4 hours. ECG is suggestive of atrial fibrillation. He is hemodynamically stable. What is the next best step in management?
Options:
A) Emergency cardioversion
B) Control ventricular rate
C) Echocardiography to look for left atrial clot
D) Start low molecular weight heparin
Correct Answer: B) Control ventricular rate
NEET PG 2025 Microbiology Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical question
A farmer presents with an ulcerative skin lesion with central necrosis. A smear from the lesion, stained with polychrome methylene blue, shows capsulated bacilli positive for the M’Fadyean reaction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Yersinia pestis
C) Clostridium perfringens
D) Chlamydia trachomatis
Correct answer: A) Bacillus anthracis
Question 2
Clinical question
A 32‑year‑old farmer presents with high‑grade fever, severe myalgia, and redness of the eyes. Investigations reveal elevated bilirubin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Brucellosis
B) Weil’s syndrome
C) Malaria
D) Enteric fever
Correct answer: B) Weil’s syndrome
Question 3
Clinical question
A 19‑year‑old college student presents with sudden‑onset fever, headache, vomiting, and a rapidly spreading purpuric rash. He appears confused, and his BP is measured to be 80/50 mmHg, HR 120/min, and Temp 39.5°C. On examination, he has petechiae and purpura over his lower limbs and trunk. He succumbs to his illness, and an autopsy is carried out. The gross specimen of the brain is shown below. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely cause of his condition?
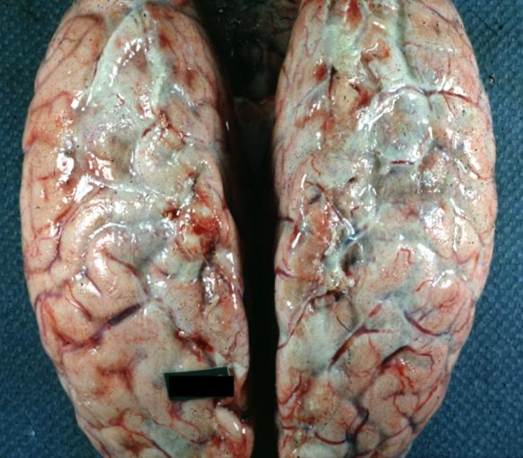
Options:
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
B) Haemophilus influenzae type B
C) Neisseria meningitidis
D) Listeria monocytogenes
Correct answer: C) Neisseria meningitidis
Question 4
Clinical question
A 35‑year‑old man presents with a 2‑week history of low‑grade fever, nonproductive cough, weight loss, and fatigue. Chest X‑ray shows bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy with patchy infiltrates. A lactophenol cotton blue mount from the sputum culture appears as below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
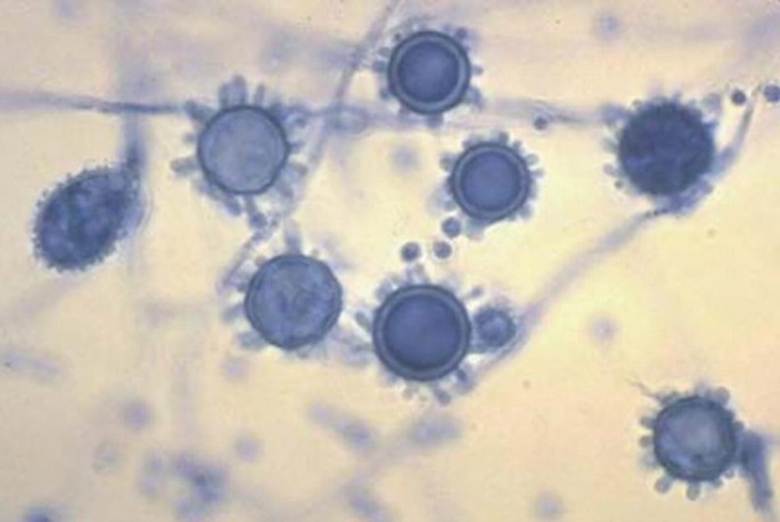
Options:
A) Pulmonary tuberculosis
B) Histoplasmosis
C) Coccidioidomycosis
D) Blastomycosis
Correct answer: B) Histoplasmosis
Question 5
Non-clinical question
Group A Streptococcus is the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis in school-aged children. Which of the following bacterial components is primarily responsible for its attachment to fibronectin on the epithelial lining of the pharynx?
Options:
A) Lipoteichoic acid
B) Capsule
C) Flagella
D) Lipoprotein
Correct answer: A) Lipoteichoic acid
Question 6
Clinical question
A child presents with intense perianal itching, especially at night. On examination, thread‑like white worms are seen in the perianal region, and the microscopic examination is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
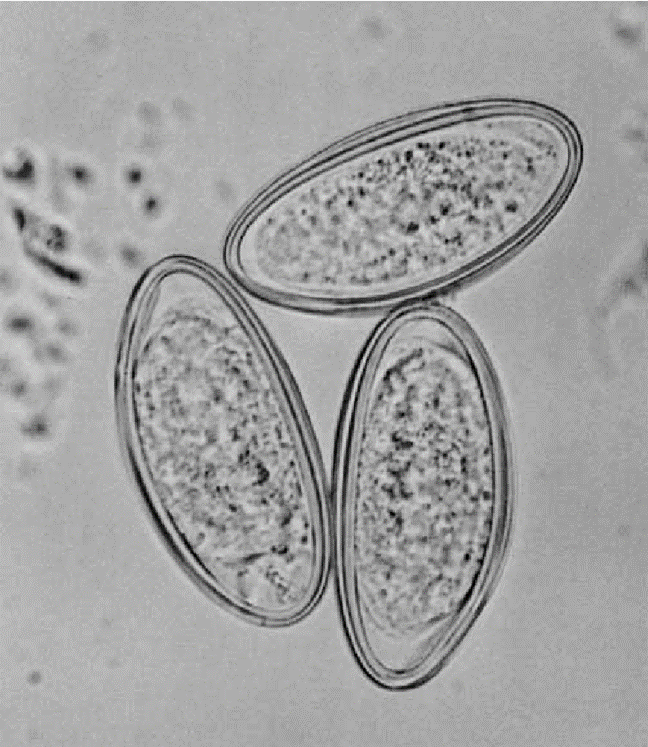
Options:
A) Enterobius vermicularis
B) Ancylostoma duodenale
C) Trichuris trichura
D) Ascaris lumbricoides
Correct answer: A) Enterobius vermicularis
Question 7
Clinical question
A child presents with painful vesicular lesions near the mouth. Tzanck
smear reveals multinucleated giant cells with intranuclear inclusions. What is the most likely
causative organism?
Options:
A) Cytomegalovirus
B) Herpes simplex virus
C) Varicella-zoster virus
D) Molluscum contagiousm virus
Correct answer: B) Herpes simplex virus
Question 8
Clinical question
A male patient presents with fever, cough, and hemoptysis. Microscopic examination of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid shows septate hyphae with acute-angle dichotomous branching. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Mucormycosis
B) Histoplasmosis
C) Aspergillosis
D) Candidiasis
Correct answer: C) Aspergillosis
Question 9
Clinical question
A middle-aged man from a tropical region presents with progressive swelling of the lower limb. A peripheral blood smear is shown below. What is the most likely cause of his limb swelling?
Options:
A) Hypoalbuminemia
B) Lymphatic obstruction
C) Hypoproteinemia
D) Increased hydrostatic pressure
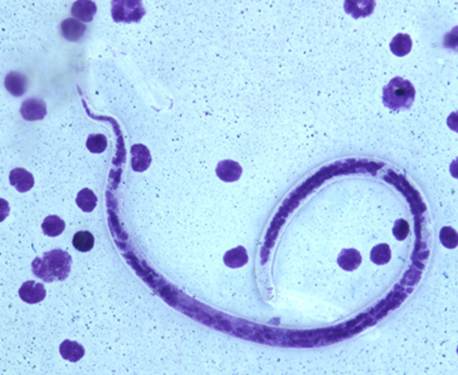
Correct answer: B) Lymphatic obstruction
Question 10
Clinical question
A patient presents with chronic meningitis. Laboratory findings reveal Gram-positive, filamentous branching bacteria which are weakly acid-fast with modified Ziehl–Neelsen (ZN) stain. The paraffin bait technique is used to isolate the organism. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Options:
A) Actinomyces israeli
B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C) Nocardia asteroides
D) Cryptococcus neoformans
Correct answer: C) Nocardia asteroides
Question 11
Clinical question
In a village, several people develop dysentery after consuming raw milk. Laboratory examination of stool samples reveals: Gram-negative, curved rods with predominant polymorphonuclear infiltration. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Options:
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Staphylococcus aureus
C) Vibrio parahaemolyticus
D) Campylobacter jejuni
Correct Answer: D) Campylobacter jejuni
Question 12
Clinical question
A patient presents with a long-standing swelling and discharging sinuses on the foot as shown below. The discharge contains black granules. What is the most likely finding on the KOH mount?
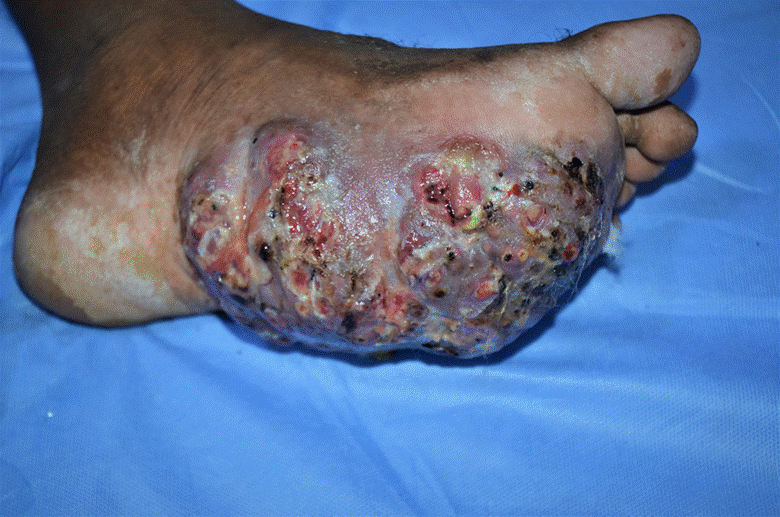
Options:
A) Small spores and pseudohyphae
B) Arthrospores
C) Septate hyphae with 4-5 microns in width
D) Filamentous branching bacteria
Correct Answer: C) Septate hyphae with 4-5 microns in width
NEET PG 2025 OBG Previous Year Questions
Q.1
Clinical Question:
In a woman with a regular 28-day menstrual cycle, which of the following best describes the typical hormonal profile during days 21 to 25 of the cycle?
Options:
- Low estrogen, high progesterone, low LH and FSH
- Low estrogen, low progesterone, low FSH and LH
- Low estrogen, high progesterone, high FSH and LH
- High estrogen, high progesterone, low FSH and LH
Correct Answer: D) High estrogen, high progesterone, low FSH and LH
Q.2
Clinical Question:
Identify the manoeuvre shown in the given image.
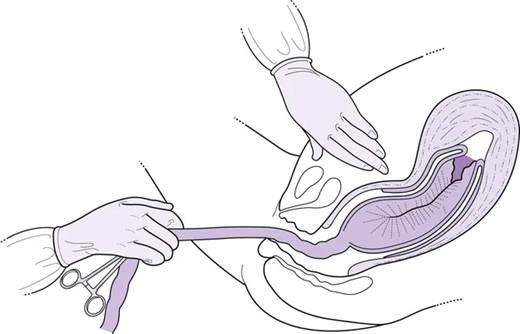
Options:
- Manual removal of placenta
- Controlled cord traction
- Uterine massage
- Bimanual compression of the uterus
Correct Answer: B) Controlled cord traction
Q.3
Clinical Question:
A 32-year-old woman with an obstetric score of P2L2 presents with 6 months of secondary amenorrhea. Laboratory evaluation shows FSH 36 mIU/mL, LH 56 mIU/mL, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) 0.05 ng/mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperprolactinemia
Correct Answer: B) Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
Q.4
Clinical Question:
A 28-year-old woman in labour is undergoing per vaginal examination, and a pulsating umbilical cord is felt below the presenting part. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Options:
- Elevate buttocks, push the presenting part upward, and fill the bladder
- Attempt to reposition the cord into the vagina and vaginal packing
- Wait and watch with close monitoring
- Augment labor with oxytocin
Correct Answer: A) Elevate buttocks, push the presenting part upward, and fill the bladder
Q.5
Clinical Question:
A G2P1L1 with a history of a previous cesarean section is undergoing a trial of labor and presents in active labor. During labor, there is fetal bradycardia and maternal tachycardia. Persistent suprapubic pain between contractions is also noted. On examination, the cervix is 8 cm dilated, and the vertex is at -1 station. What is the next best step in management?
Options:
- Emergency lower segment cesarean section
- Artificial rupture of membranes
- Augment labor with oxytocin
- Attempt instrumental vaginal delivery
Correct Answer: A) Emergency lower segment cesarean section
Q.6
Clinical Question:
In the repair of a mediolateral episiotomy, what is the correct order of tissue approximation during suturing?
Options:
- Mucosa → Muscle → Skin
- Skin → Mucosa → Muscle
- Muscle → Skin → Mucosa
- Skin → Muscle → Mucosa
Correct Answer: A) Mucosa → Muscle →
Q.7
Clinical Question:
A patient presents with 2 months of amenorrhea and an enlarged uterus. On examination, there is darkening of the areola, prominent Montgomery’s tubercles, a linea nigra is present, and there is bluish discoloration of the vagina on per-vaginal examination. How would you categorize these signs of pregnancy?
Options:
- Presumptive signs of pregnancy
- Probable signs of pregnancy
- Positive signs of pregnancy
- Diagnostic signs of pregnancy
Correct Answer: B) Probable signs of pregnancy
Q.8
Clinical Question:
Hydronephrosis due to the extension of a cervical tumor is a criterion for which FIGO stage of cervical cancer?
Options:
- Stage IIIA
- Stage IIIB
- Stage IVA
- Stage IVB
Correct Answer: B) Stage IIIB
Q.9
Clinical Question:
A woman presents with abdominal distension and ascites. On examination, the abdomen is enlarged, and CA-125 levels are elevated. Imaging shows a large multicystic ovarian mass with irregular septations. What is the most likely diagnosis?

Options:
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma
- Granulosa cell tumor
- Simple serous cystadenoma
- Mucinous cystadenoma
Correct Answer: A) Serous cystadenocarcinoma
Q.10
Clinical Question:
A woman develops atonic postpartum hemorrhage that does not respond to initial measures and medical management. What is the next best step in management that can be done in the labour room?
Options:
- Intrauterine balloon tamponade
- Uterine artery ligation
- Internal iliac artery ligation
- Compression sutures
Correct Answer: A) Intrauterine balloon tamponade
Q.11
Clinical Question:
A primigravida undergoing vaginal delivery develops shoulder dystocia after delivery of the fetal head. Which of the following is the correct sequence of maneuvers used in its management?
Options:
- McRoberts → Rubin → Gaskin → Zavanelli
- Zavanelli → McRoberts → Gaskin → Rubin
- Rubin → McRoberts → Gaskin → Zavanelli
- Gaskin → Rubin → McRoberts → Zavanelli
Correct Answer: A) McRoberts → Rubin → Gaskin → Zavanelli
Q.12
Clinical Question:
A woman, P2L2, with a history of difficult vaginal deliveries conducted by an untrained attendant, now presents with the complaint of “something coming out of her vagina.” On examination, the finding is as shown in the image below. Injury to which of the following ligaments is most likely responsible for this condition?
Options:
- Sacrospinous ligament
- Mackenrodt’s ligament
- Broad ligament
- Round ligament
Correct Answer: B) Mackenrodt’s ligament
Q.13
Clinical Question:
During an assisted breech delivery, the attending identified winging of the scapula and performed the following manoeuvre. Identify this.
Options:
- Lovset maneuver
- Burn-Marshall maneuver
- Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver
- Pinard’s maneuver
Correct Answer: A) Lovset maneuver
Q.14
Clinical Question:
A 55-year-old post-menopausal woman presents to the OPD for a routine BP checkup. Her BP was 170/100 mmHg. She also complains of a blood-stained discharge per vagina. What is the next best step in management?
Options:
- Reassure her that some discharge is normal at this age
- Immediate referral to a cardiologist before any further evaluation
- Immediate pelvic examination, transvaginal sonography (TVS), and Pap smear
- Start antihypertensive medication and observe for 1 week
Correct Answer: C) Immediate pelvic examination, transvaginal sonography (TVS), and Pap smear.
Q.15
Clinical Question:
A 46-year-old nulliparous woman presents with delayed cycles and heavy bleeding for the past 1 year. Transvaginal ultrasonography reveals an endometrial thickness of 18 mm. What is the next best step in management?
Options:
- Start combined oral contraceptive pills
- Schedule hysterectomy
- Wait and watch for 6 months
- Perform endometrial biopsy
Correct Answer: D) Perform endometrial biopsy
Q.16
Clinical Question:
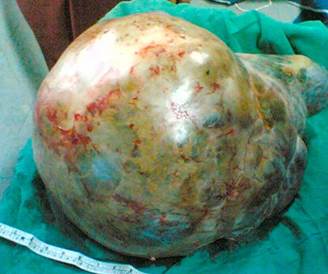
A 65-year-old postmenopausal female presents with a chief complaint of vaginal bleeding for the past three months. She undergoes a hysterectomy, and the gross specimen is shown below. Based on the image and clinical scenario, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
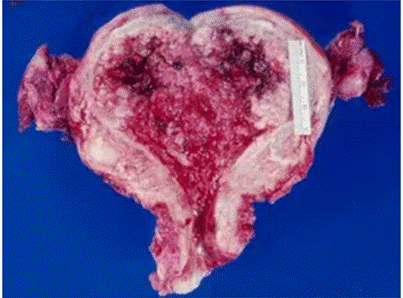
Options:
- Endometrial cancer
- Fibroid
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
Correct Answer: A) Endometrial cancer
Q.17
Clinical Question:
A woman presents for her first antenatal visit and reports that her LMP was approximately 2 months ago. Which ultrasound parameter is the most accurate for dating the pregnancy at this stage?
Options:
- Biparietal Diameter (BPD)
- Crown-Rump Length (CRL)
- Femur Length (FL)
- Abdominal Circumference (AC)
Correct Answer: B) Crown-Rump Length (CRL)
Q.18
Clinical Question:
A primigravida at 37 weeks presents with decreased fetal movements for one day. A Nonstress Test (NST) showed one acceleration in 20 minutes and no decelerations. What is the next step in management?
Options:
- Continue NST for 40 minutes
- Induce labour immediately
- Emergency LSCS
- Instrumental delivery
Correct Answer: A) Continue NST for 40 minutes
Q.19
Clinical Question:
A 42-year-old woman presents with chronic lower abdominal pain and dysmenorrhea. MRI is
as shown. What is the most likely diagnosis?
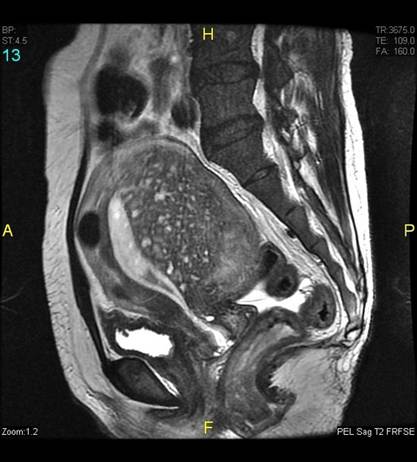
Options:
- Intramural fibroid
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Endometriosis
Correct Answer: B) Adenomyosis
Q.20
Clinical Question:
A pregnant female gives a history of toxoplasma infection 5 years ago and currently tests positive for IgG antibodies. On examination, lymphadenopathy is noted. What is the next step in management?
Options:
- Reassure and continue the pregnancy
- Carry out an MTP
- Counsel her about the potential teratogenic effects of the infection
- Treat the female for toxoplasmosis
Correct Answer: A) Reassure and continue the pregnancy
NEET PG 2025 Ophthalmology Previous Year Questions
Q.1
Clinical Question:
A 15-year-old girl presents with a painless swelling in the right supraorbital region that has been gradually progressing over the past year. What is the most likely diagnosis?

Options:
- Lacrimal gland mass
- Dermoid cyst
- Hemangioma
- Epidermoid cyst
Correct Answer: B) Dermoid cyst
Q.2
Clinical Question:
A patient presents with guttate lesions in one eye and bullous keratopathy in the other eye. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Options:
- Trichoma
- Herpes keratitis
- Fuchs endothelial dystrophy
- Keratoconus
Correct Answer: C) Fuch’s endothelial dystrophy
Q.3
Clinical Question:
Which of the following statements regarding orbital cellulitis is true?
Options:
- Ethmoidal sinusitis is the most common source of infection in all age groups
- Topical broad-spectrum antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment
- The inflammation is restricted anterior to the orbital wall
- Patients characteristically present with proptosis, blurring of vision, normal pupillary and ocular movements
Correct Answer: A) Ethmoidal sinusitis is the most common source of infection in all age groups
Q.4
Clinical Question:
A 65-year-old male presents with complaints of a decrease in vision. There were white deposits on the anterior lens surface, seen during slit lamp examination. What is the most likely diagnosis?
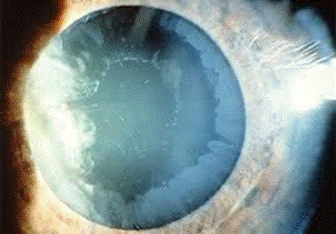
Options:
- Glaucomflecken with acute angle closure glaucoma
- Pseudoexfoliation syndrome
- iritis with pupillary deposits
- Anterior capsule opacification
Correct Answer: B) Psedoexfoliation syndrome
Q.5
Non-clinical Question:
Which of the following conditions is treated using the modality shown in the image?
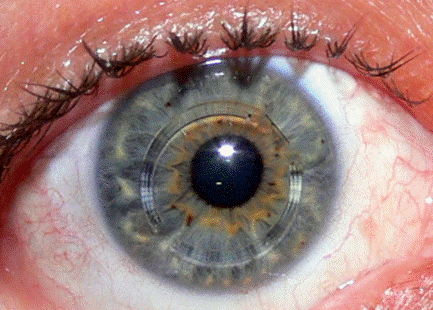
Options:
- Keratoconus
- Keratoglobus
- Vogt’s limb striae
- Corneal dystrophy
Correct Answer: A) Keratoconus
Q.6
Clinical Question:
Binocular single vision consists of which of the following components, corresponding to Image A and Image B, respectively?
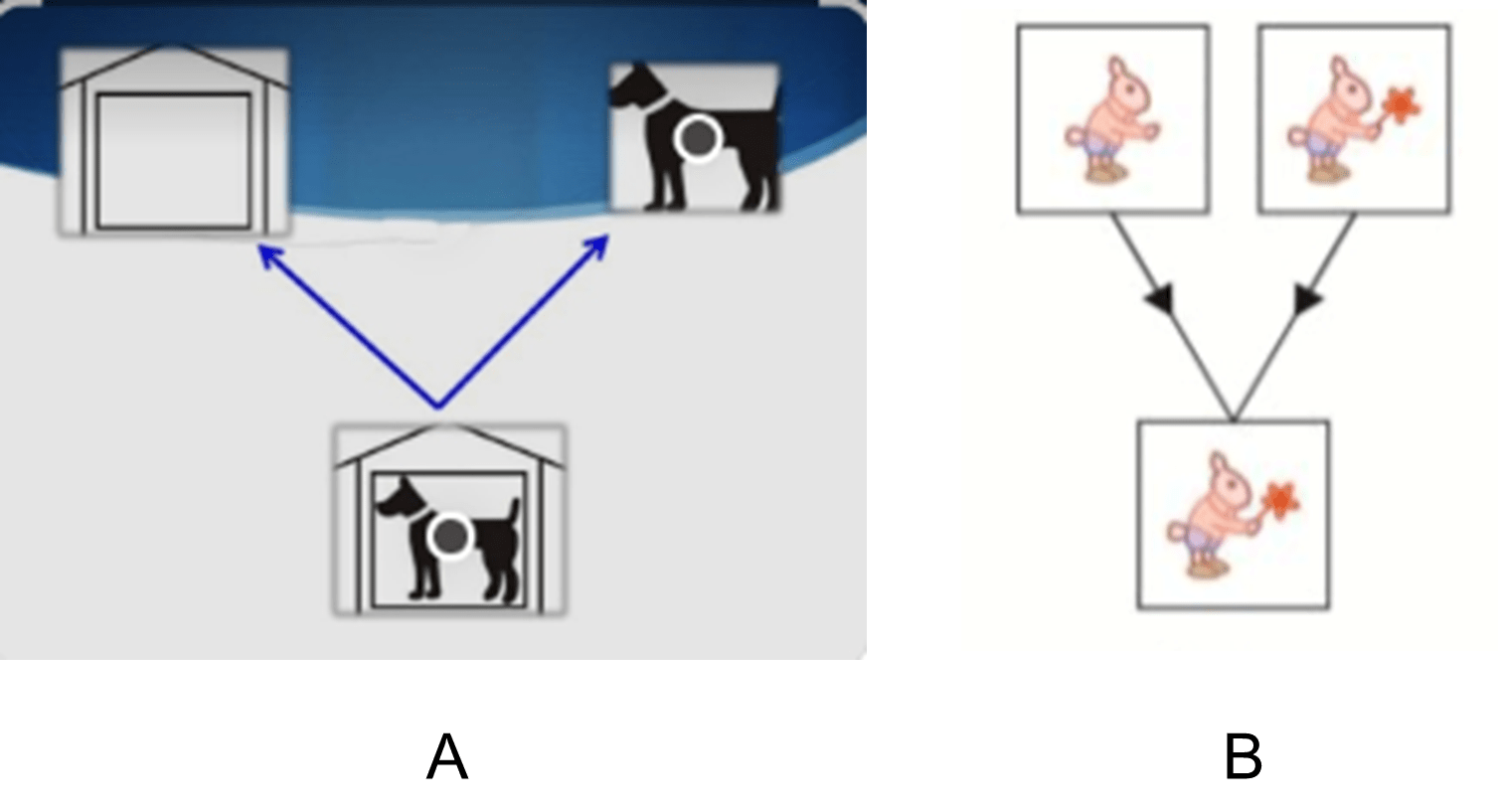
Options:
- Fusion and stereopsis
- Fusion and simultaneous macular perception
- Simultaneous macular perception and stereopsis
- Simultaneous macular perception and fusion
Correct Answer: D) Simultaneous macular perception and fusion
NEET PG 2025 Orthopaedics Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical question
A 26-year-old male presents with complaints of chronic lower back pain, which has been progressive for the past 1 year. He also experiences early morning stiffness lasting for 1.5 hours, which is relieved by exercise. He also gives a history of anterior uveitis. Which of the following investigations is most useful for early diagnosis of the underlying condition?
Options:
A) Anti-CCP
B) MRI of the sacroiliac joint
C) CT spine of the sacroiliac joint
D) Bone scan
Correct answer: B) MRI of sacroiliac joint
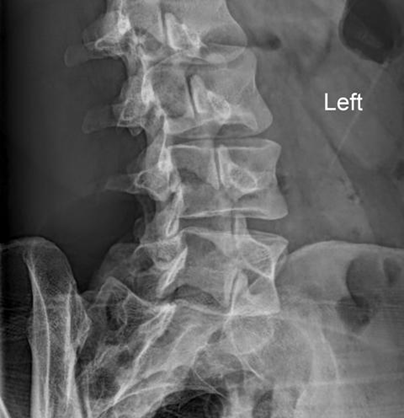
Question 2
Clinical question
A 66-year-old female presents with chronic lower back pain. An oblique lumbar spine X-ray is done and shown below. Based on the radiological findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Spondylolysis
B) Spondylolisthesis
C) Crush vertebral fracture
D) Klippel Feil syndrome
Correct answer: A) Spondylolysis
Question 3
Clinical question
A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department following a motorbike accident and is found to have a closed midshaft fracture of the left tibia. Six hours later, he develops severe leg pain that is disproportionate to the injury and worsens with passive dorsiflexion of the foot. The pain is not relieved by analgesics. On examination, dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are present, but there is no sensation over the first dorsal web space. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Options:
A) Administer opioid analgesics and observation
B)Elevation of limb and observation
C) Immediate fasciotomy
D) Apply cast and follow-up
Correct answer: C) Immediate fasciotomy
Question 4
Clinical question
A 24-year-old male sustained a shaft of femur fracture after a road traffic accident, and internal fixation was done for the same. Two days later, he developed shortness of breath with confusion and a petechial rash. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Fat embolism
B) Tension pneumothorax
C) Air embolism
D) ARDS
Correct answer: A) Fat embolism
Question 5
Clinical question
A 70-year-old man undergoes routine blood work as part of a health check-up. He has no major complaints except for occasional bone pain. He denies weakness or recent fractures. On physical examination, no focal deficits are noted.
His biochemical profile is as follows:
Serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP): 710 IU/L (↑ elevated)
Serum calcium: 9.2 mg/dL (Normal)
Serum phosphate: 3.5 mg/dL (Normal)
25-hydroxy vitamin D: Normal
Parathyroid hormone (PTH): Normal
X-ray pelvis shows thickened cortices with areas of sclerosis and lysis.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Osteomalacia
B) Primary hyperparathyroidism
C) Paget’s disease
D) Osteoporosis
Correct answer: C) Paget’s disease
NEET PG 2025 Pathology Previous Year Questions
Question 1
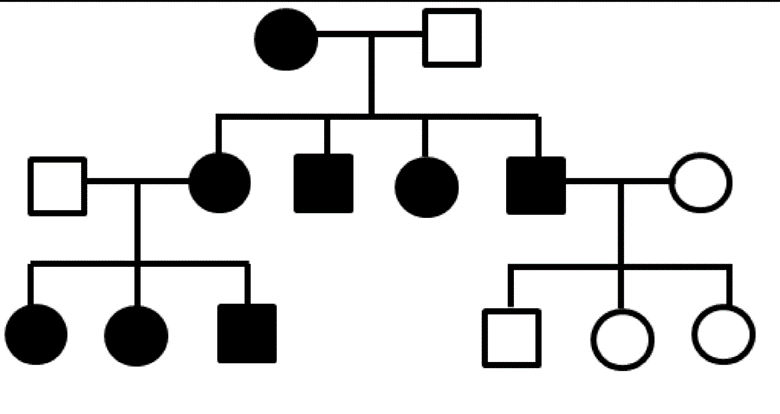
Non-clinical question:
Which of the following conditions follows the inheritance pattern shown in the given pedigree chart?
Options:
A) Achondroplasia
B) Kearns-Sayre syndrome
C) Williams syndrome
D) Prader-Willi syndrome
Correct answer: B) Kearns-Sayre syndrome
Question 2
Clinical question:
A patient presents with recurrent episodes of disseminated gonococcal infection. A joint aspirate during an episode of joint pain reveals Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Which of the following could be the underlying mechanism?
Options:
A)Myeloperoxidase deficiency
B) PMN cell chemotactic defect
C) Terminal complement deficiency
D) C2 deficiency
Correct answer: C) Terminal complement deficiency
Question 3
Clinical question
A patient presents with long limbs and ectopia lentis. His arm span is found to be greater than his height. Marfan syndrome is suspected. Which of the following gene defects is most likely responsible?
Options:
A) PLOD1
B) Elastin
C) Fibrillin
D) COLA1
Correct answer: C) Fibrillin
Question 4
Clinical question
A 45-year-old female presents with a 2-year history of progressive unilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, and ataxia. An MRI imaging of the brain reveals a well-defined tumour located in the cerebellopontine angle (CPA). A surgical resection is performed, and subsequent histopathological examination of the tumour reveals Antoni A and B areas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Meningioma
B) Ependymoma
C) Schwannoma
D) Vestibular neuritis
Correct answer: C) Schwannoma
Question 5
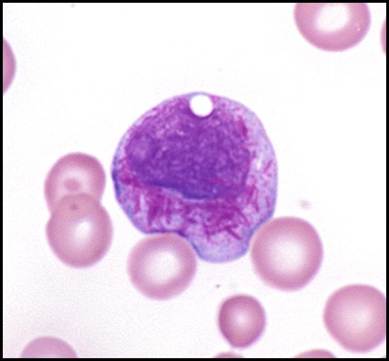
Clinical question
An elderly male presents with cervical lymph node enlargement and increased bleeding tendency. Bone marrow examination reveals >25% blasts, and the peripheral smear is as shown below. Which of the following cytogenetic abnormalities is most likely associated with this condition?
Options:
A) Inv (16)
B) t(15;17)
C) t(8;21)
D) t(9;22)
Correct answer: B) t(15;17)
Question 6
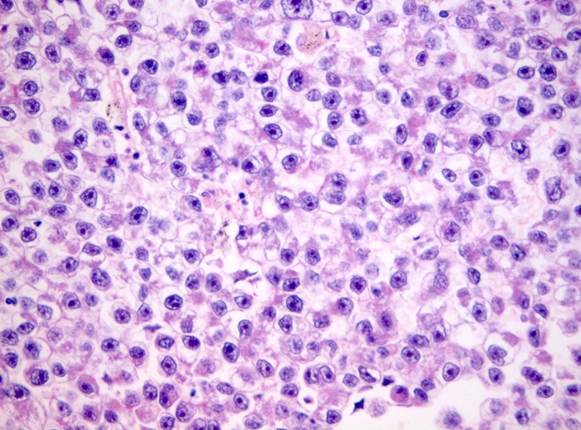
Clinical question
An elderly male presents with progressive, painless testicular swelling. Gross examination of the testis shows a multinodular, homogeneous, gray-white mass without haemorrhage or necrosis. Histopathological examination is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Yolk sac tumour
B) Seminoma
C) Embryonal carcinoma
D) Leydig cell tumour
Correct answer: B) Seminoma
Question 7
Clinical question
A patient presents with a midline neck swelling. Histology showed amyloid deposition, and immunohistochemistry is positive for synaptophysin, chromogranin, and TTF‑1. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Papillary thyroid cancer
B) Medullary thyroid cancer
C) Follicular thyroid cancer
D) Anaplastic thyroid cancer
Correct answer: B) Medullary thyroid cancer
Question 8
Non-clinical question
A gross specimen of the liver shows a well-circumscribed lesion, as shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
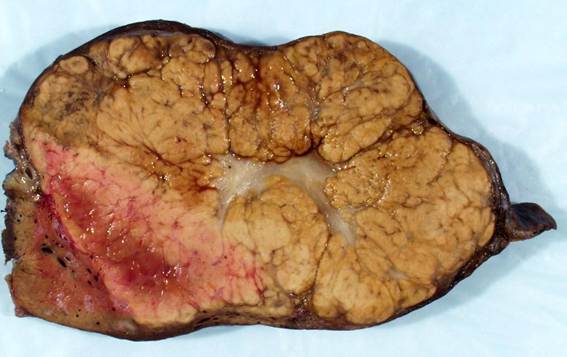
Options:
A) Hepatocellular adenoma
B) Hepatocellular carcinoma
C) Focal nodular hyperplasia
D) Regenerative nodule
Correct answer: C) Focal nodular hyperplasia
Question 9
Clinical question
An elderly male presents with bilateral cervical lymph node enlargement. Histopathological examination reveals small cleaved cells as well as larger cells with open chromatin. Immunohistochemistry reveals CD10-positive and BCL2-positive cells. Which of the following cytogenetic abnormalities is most commonly associated with this condition?
Options:
A) t(11;18)
B) t(14;18)
C) t(11;14)
D) t(8;14)
Correct answer: B) t(14;18)
Question 10
Non-clinical question
Which of the following are caspase-mediated forms of cell death?
Options:
A) Apoptosis and necroptosis
B) Apoptosis and necrosis
C) Apoptosis and pyroptosis
D) Apoptosis and ferroptosis
Correct answer: C) Apoptosis and pyroptosis
Question 11
Clinical question
A patient presents with mild anaemia and jaundice. Examination reveals splenomegaly. Laboratory findings show an elevated mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC). His father has also had a similar clinical history. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Hereditary spherocytosis
B) Iron deficiency anaemia
C) Autoimmune hemolytic anaemia
D) Thalassemia minor
Correct answer: A) Hereditary spherocytosis
Question 12
Clinical question
An 8-year-old child presents with progressive vision loss, and an MRI was done, which showed a suprasellar mass. Histopathology of the mass showed the findings of palisading epithelium and wet keratin. Which among the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Craniopharyngioma
B) Pituitary adenoma
C) Rathke’s cleft cyst
D) Meningioma
Correct answer: A) Craniopharyngioma
Question 13
Clinical question
An elderly patient presents with fatigue, generalised lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly. After examination and laboratory investigations, a diagnosis of CLL is made. Which of the following laboratory techniques is most useful to compare and quantify CD markers on cells?
Options:
A) ELISA
B) Western blot
C) Flow cytometry
D) Immunohistochemistry
Correct answer: C) Flow cytometry
Question 14
Non-clinical question
Antimitochondrial antibody (AMA) positivity is most strongly associated with which of the following conditions?
Options:
A) Primary biliary cholangitis
B) Autoimmune hepatitis
C) Sarcoidosis
D) Wilson’s
Correct answer: A) Primary biliary cholangitis
Question 15
Clinical question
A patient presents with a 1‑month history of cough, chest pain, and dyspnea. Imaging reveals bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Biopsy of a mediastinal lymph node shows non‑caseating granulomas containing stellate inclusions. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Tuberculosis
B) Sarcoidosis
C) Lung cancer
D) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Correct answer: B) Sarcoidosis
Question 16
Clinical question
A 45-year-old man presents with rapidly progressive swelling, pain, foul-smelling discharge, and discolouration of the hand following a traumatic injury, as shown in the image given below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
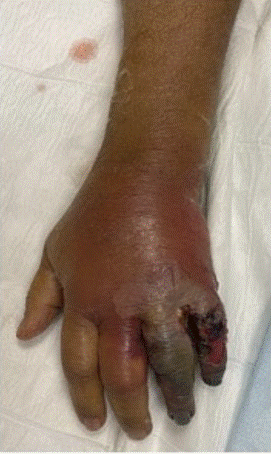
Options:
A) Wet gangrene
B) Dry gangrene
C) Infectious tenosynovitis
D) Raynaud’s phenomenon
Correct answer: A) Wet gangrene
Question 17
Clinical question
A middle-aged woman presents with dry eyes and dry mouth. Laboratory tests reveal positive anti-Ro (SSA) and anti-La (SSB) antibodies. What is the most likely underlying pathological mechanism?
Options:
A) Destruction of exocrine glands by neutrophils
B) IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
C) Lymphocytic infiltration and destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands
D) Deposition of amyloid in salivary glands
Correct answer: C) Lymphocytic infiltration and destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands
Question 18
Clinical question
A 36-year-old male patient with gluten sensitivity presents with intensely itchy, grouped vesicular lesions on the extensor surfaces. A skin biopsy with direct immunofluorescence shows the following finding. What is the most likely diagnosis?
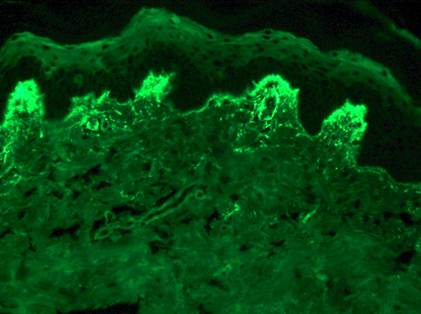
Options
A) Bullous pemphigoid
B) Pemphigus vulgaris
C) Dermatitis herpetiformis
D) Psoriasis
Correct answer: C) Dermatitis herpetiformis
Question 19
Clinical question
A patient presents with a persistent red lesion on the lateral border of the tongue. Biopsy confirms squamous cell carcinoma. Which of the following viral infections is most strongly associated with this malignancy?
Options:
A) Epstein–Barr virus
B) Cytomegalovirus
C) Herpes simplex virus
D) Human papillomavirus
Correct answer: D) Human papillomavirus
Pediatrics
NEET PG 2025 Pediatrics Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical question
A 2-year-old child is brought to the emergency room with a generalised seizure following a high-grade fever. What is the first-line drug of choice for seizure control in this
setting?
Options:
A) Diazepam
B) Ethosuximide
C) Valproate
D) Phenytoin
Correct answer: A) Diazepam
Question 2
Clinical question
A 3-year-old boy presents with fever and cough. A chest x-ray was done, which showed the following findings. Which of the following is the most likely underlying pathology?
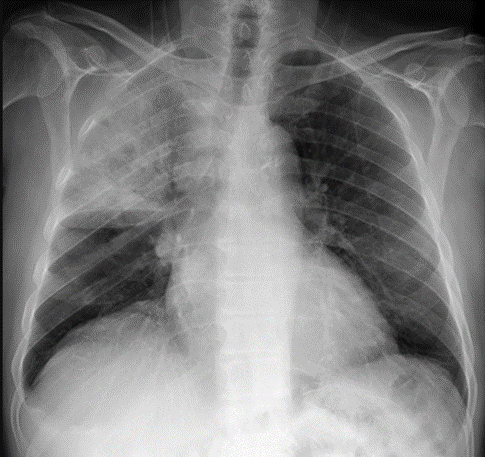
Options:
A) Right upper lobe collapse
B) Right upper lobe abscess
C) Right upper lobe consolidation
D) Bronchogenic carcinoma
Correct answer: C) Right lobe consolidation
Question 3
Clinical question
A pregnant woman is diagnosed with HIV infection at 34 weeks of gestation. Her viral load was 1200 copies/mL, and she was then started on ART. She delivers a 2.5 kg term baby at 38 weeks. What is the most appropriate postnatal prophylaxis for the newborn?
Options:
A) Both nevirapine and zidovudine for 12 weeks, along with exclusive breast milk feeding
B) Nevirapine for 6 weeks with exclusive breastfeeding
C) No breastfeeding and initiate exclusive formula feeding
D) Nevirapine prophylaxis for 6 weeks
Correct answer: A) Both nevirapine and zidovudine for 12 weeks, along with exclusive breast milk feeding
Question 4
Clinical question
Which of the following is most likely in a neonate presenting with congenital hypothyroidism, decreased T3 and T4 levels, decreased radioactive iodine uptake, but a normal thyroid on ultrasound?
Options:
A) Thyroid dyshormonogenesis
B) Thyroid agenesis
C) Iodine deficiency
D) Defect in iodine transport
Correct answer: D) Defect in iodine transporter
Question 5
Clinical question
During examination of a neonate, an index finger was found missing along with multiple deformities of all four limbs, as shown in the image given below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
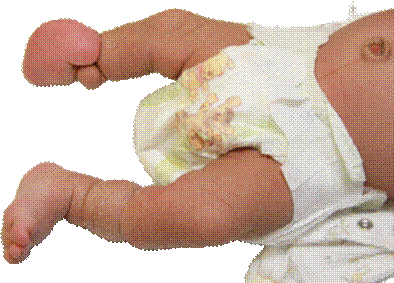
Options:
A) Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita
B) CTEV
C) Amniotic band syndrome
D) Syndactyly
Correct answer: C) Amniotic band syndrome
NEET PG 2025 Pharmacology Previous Year Questions
Question: 1
Clinical question
A 38-year-old female presents with a pounding headache, palpitations, and sweating for 2 months. Each episode lasts for 20 minutes and is triggered by stress or physical exertion. Her pulse is 112/min, BP is 180/100 mm Hg, and urine shows elevated VMA and normetanephrines. MRI reveals a right adrenal mass. Which drug can be used both pre- and intra-operatively?
Options:
A) Esmolol
B) Phenoxybenzamine
C) Nifedipine
D) Clonidine
Correct Answer: B) Phenoxybenzamine
Question 2
Non-clinical question
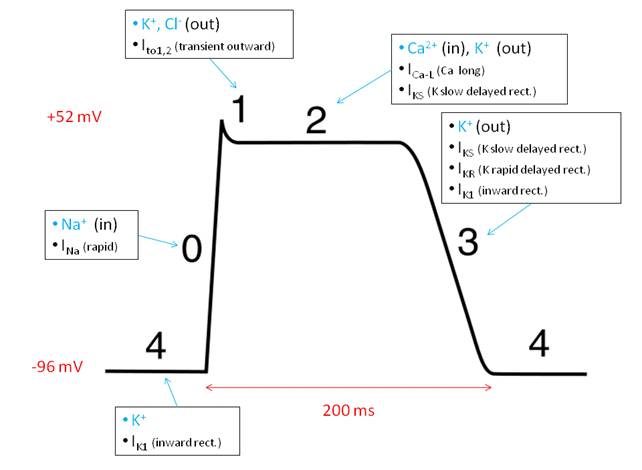
In the given cardiac action potential graph, identify the phase where amiodarone acts.
Options:
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
Correct Answer: D) 3
Question: 3
Clinical question
A patient with tumour lysis syndrome has elevated uric acid levels. What is the mechanism of action of pegloticase?
Options:
- Oxidises uric acid
- Hydrolyses uric acid
- Inhibits xanthine oxidase
- Inhibits URAT-1 transporters in the kidney
Correct Answer: A) Oxidises uric acid
Question: 4
Clinical question
A female patient with HIV infection (CD4 count 150 cells/mm³) was newly diagnosed with rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis. What anti-tubercular treatment regimen should be initiated, and which HIV-related complication should you look out for?
Options:
- Isoniazid, levofloxacin, ethambutol, clarithromycin – QT prolongation
- Isoniazid, levofloxacin, ethambutol, pyrazonamide – hepatotoxicity
- Isoniazid, ethambutol, pyrazinamide – optic neuritis
- BPaLM regimen – IRIS
Correct Answer: D) BPaLM regimen – IRIS
Question: 5
Clinical question
Which of the following drugs is most appropriate to be started in a diabetic patient with an HbA1c of 8.8 mmol/L with heart failure who is already on metformin and insulin glargine?
Options:
- Pioglitazone
- Empagliflozin
- Glibenclamide
- Sitagliptin
Correct Answer: B) Empagliflozin
Question 6
Clinical question
A 32-year-old woman with a BMI of 38 kg/m² undergoes an elective lower segment cesarean section (LSCS) at 35 weeks due to preeclampsia. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacological method for DVT prophylaxis in this patient?
Options:
- Aspirin
- Clopidogrel
- Warfarin
- LMWH
Correct Answer: D) LMWH
Question 7
Clinical question
What is the mechanism of renal calculi formation in a patient on Hydrochlorothiazide?
Options:
- Increased calcium excretion
- Decreased calcium excretion
- Increased oxalate absorption
- Decreased citrate excretion
Correct Answer: D) Decreased citrate excretion
Question 8
Non-clinical question
In the Pritchard regimen for the management of eclampsia, what is the loading dose of magnesium sulfate?
Options:
- 10
- 14
- 4
- 20
Correct Answer: B) 14
Question 9
Clinical question
A patient is diagnosed with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia and requires prophylaxis for the same. Which of the following drugs is appropriate for this patient?
Options:
- IV adenosine
- IV esmolol
- Oral phenytoin
- Oral verapamil
Correct Answer: D) Verapamil
Question 10
Clinical question
A female diagnosed with migraine presents to the OPD and complains of 4-5 episodes per month, with each episode lasting 24-48 hours. She also experiences anxiety and palpitations. She experiences partial pain relief with OTC NSAIDs and was started on sumatriptan prophylaxis, but developed chest tightness and flushing. She has no history of cardiac illnesses, but there is a positive family history of coronary artery disease. Which of the following drugs can be used for prophylaxis in this patient?
Options:
- Naratriptan
- Propranolol
- Topiramate
- Ergotamine
Correct Answer: B) Propranolol
Question 11
Clinical question
A 60-year-old man with chronic kidney disease presents with complaints of increasing
fatigue, dyspnea on exertion, and signs of congestive heart failure. On evaluation, he is found to have anaemia. Which of the following drugs is appropriate for this patient?
Options:
- Parenteral iron
- Folic acid
- Filgastrim
- Darbepoietin-alpha
Correct Answer: D) Darbepoietin-alpha
Question 12
Non-clinical question
Benralizumab, a monoclonal antibody used to treat asthma, acts against which of the following?
Options:
- IL-1
- IL-4
- IL-5
- TNF alpha
Correct Answer: C) IL-5
Question 13
Clinical question
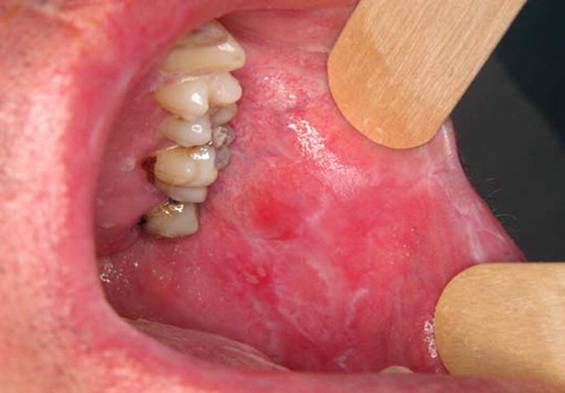
A patient presents with complaints of patches in the oral mucosa, as shown below, with a burning sensation on taking spicy food for the past 6 months. Which of the following drugs can cause this side effect?

Options:
A) Ciprofloxacin
B) Fluconazole
C) Beta blockers
D) Lithium
Correct Answer: C) Beta blockers
Question 14
Clinical question
A patient presents with symptoms of GERD. Which of the following drugs increases the tone of the LES and increases gastric emptying?
Options:
- Sodium alginate
- Pantoprazole
- Metoclopramide
- Vonoprazan
Correct Answer: C) Metoclopramide
NEET PG 2025 Physiology Previous Year Questions
Q.1
Clinical Question:
A 22-year-old college student flies to Leh, which is at an altitude of 3700 m above sea level. She experiences nausea, headache, mental confusion, and blurred vision. Which of the following is the underlying mechanism for these findings?
Options:
- Increase in sympathetic activity leading to vasoconstriction of cerebral vessels, leading to transudation of fluid
- Decrease in PaO₂ leading to vasoconstriction of cerebral vessels, leading to transudation of fluid
- Decrease in PaO₂ leading to vasodilatation of cerebral vessels, leading to transudation of fluid
- Decrease in pH leading to vasodilatation of cerebral vessels, leading to transudation of fluid
Correct Answer: C) Decrease in PaO₂ leading to vasodilatation of cerebral vessels, leading to transudation of fluid
Q.2
Clinical Question:
A woman presents with complaints of secondary amenorrhea and infertility. Investigations revealed a microadenoma of the pituitary gland and hyperprolactinemia. What is the underlying mechanism by which hyperprolactinemia causes these complaints?
Options:
- Antagonistic effect of prolatin on estrogen receptors
- Decreased GnRH secretion from hypothalamus
- Increased secretion of FSH
- Increased secretion of LH
Correct Answer: B) Decreased GnRH secretion from hypothalamus
Q.3
Clinical Question:
A patient presents with nausea, vomiting, and muscle cramps. Lab tests reveal hyponatremia and hyperkalemia. On examination, there is hyperpigmentation of the skin. Which of the following hormones is directly responsible for the hyperpigmentation?
Options:
- ACTH
- Cortisol
- Aldosterone
- Renin
Correct Answer: A) ACTH
Q.4
Non-clinical Question:
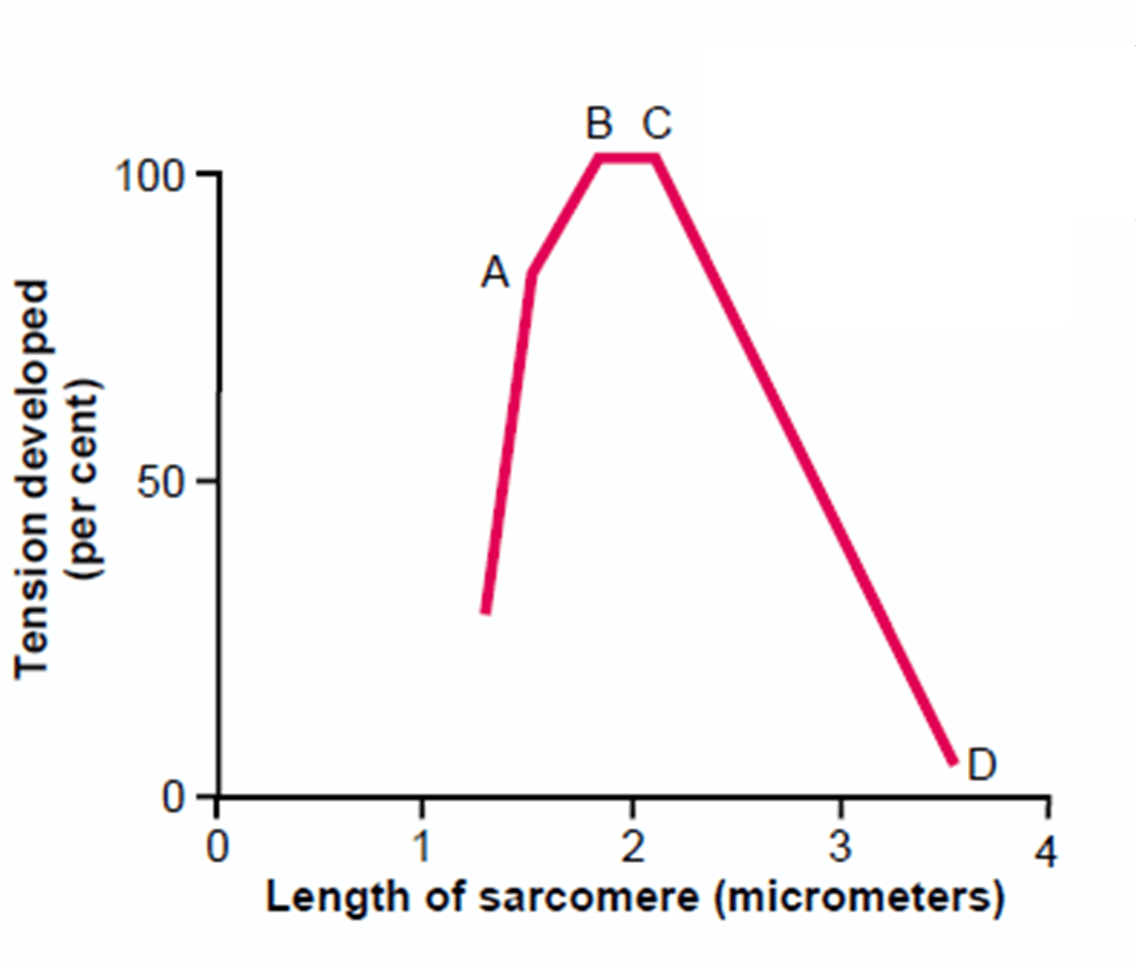
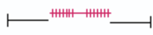
Which of the following sarcomeres corresponds to point B on the graph?
Options:
A)
B)
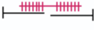
C)
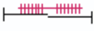
D)
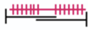
Correct Answer: Option C
Q.5
Non-clinical Question:
If there is no net transudation across a capillary with a capillary hydrostatic pressure of 18 mm Hg, capillary oncotic pressure of 27 mm Hg, and interstitial oncotic pressure of 7 mm Hg, what should be the interstitial hydrostatic pressure?
Options:
- 2 mm Hg
- -2 mm Hg
- 0 mm Hg
- 1 mm Hg
Correct Answer: B) -2 mm Hg
Q.6
Non-clinical Question:
The given graph shows PCo2 and PO2 of the right lung along with ventilation and perfusion ratio. Which point on the graph represents V/Q ratio if there is a complete block of the blood supply at alveolar level of right lung due to pulmonary embolism?
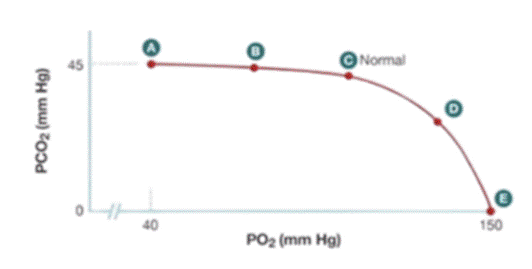
Options:
- A
- B
- D
- E
Correct Answer: D) E
NEET PG 2025 PSM Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Non-Clinical Question
According to the population strategy for prevention of cardiovascular disease, what is the recommended dietary allowance of cholesterol per day?
Options:
A) 100mg/1000 kcal
B) 200mg/1000 kcal
C) 300mg/1000 kcal
D) 400mg/1000 kcal
Correct Answer: A) 100mg/1000 kcal
Question 2
Clinical Question
A 50-year-old man from Chittoor, Andhra Pradesh, presents to the OPD with features of
osteoporosis. Examination reveals outward bending of both legs. Which of the following is not used in his management?
Options:
A) Fluoride supplementation
B) Make a surface running water source available
C) Change the source of water
D) Add alum and lime to water
Correct Answer: A) Fluoride supplementation
Question 3
Non-Clinical Question
Under Weekly Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation, what dose of iron and folic acid is given to girls 10-19 years of age:
Options:
A) 60mg elemental iron + 100mcg FA
B) 100mg elemental iron + 100mcg FA
C) 100mg elemental iron + 500mcg FA
D) 60mg elemental iron + 500mcg FA
Correct Answer: C) 100mg elemental iron + 500mcg FA
Question 4
Non-Clinical Question
There is a report of toxic fumes leaking from a nearby chemical factory. What should be your immediate action?
Options:
A) Close all doors and windows and seal your home with plastic/tape
B) Open all windows and try to ventilate the house
C) Stay inside and wait for further instructions
D) Immediately run outside without checking the wind direction or alerts
Correct Answer: A) Close all doors and windows and seal your home with plastic/tape
Question 5
Non-Clinical Question
The interval between a host receiving an infection and the period of attaining maximum infectivity is called
Options:
A) Communicable period
B) Incubation period
C) Generation time
D) Serial interval
Correct Answer: C) Generation time
Question 6
Non-Clinical Question
In an experimental study, which of the following is the correct sequence of steps?
1. Randomisation
2. Manipulation
3. Statistical analysis
4. Follow-up (checked)
Options:
A) 2,3,1,4
B) 1,2,3,4
C) 2,1,4,3
D) 1,2,4,3
Correct Answer: D) 1, 2, 4, 3
Question 7
Non-Clinical Question
For a population of 70,00,000 with 30% of it belonging to the slum population, how many Urban PHCs are required for the slum population according to NUHM?
Options:
A) 22
B) 42
C) 32
D) 52
Correct Answer: B) 42
Question 8
Non-Clinical Question
In a de facto census, individuals are counted based on:
Options:
A) Place of birth
B) Place on the date of enumeration
C) Place of employment
D) Usual place of residence
Correct Answer: B) Place on date of enumeration
Question 9
Non-Clinical Question
Which of the following tests is most appropriate to compare the mean hemoglobin levels between two independent groups?
Options:
A) Paired T test
B) Unpaired T-test
C) ANOVA
D) Chi-square test
Correct Answer: B) Unpaired T-test
Question 10
Clinical Question
A patient diagnosed with fever and dry cough was confirmed to have COVID-19. He was admitted to a district hospital and later died in the hospital. The death was registered 7 days later. What type of surveillance does this represent?
Options:
A) Active surveillance
B) Passive surveillance
C) Syndromic surveillance
D) Sentinel surveillance
Correct Answer: B) Passive surveillance
Question 11
Non-Clinical Question
Which of the following vaccines will you use in your PHC?
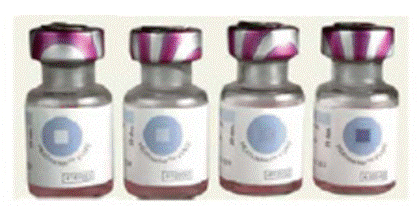
Options:
A) 1, 2
B) 2, 3
C) Only 1
D) 3, 4
Correct Answer: A) 1, 2
Question 12
Non-Clinical Question
A mosquito larva is examined under a hand lens. It showed no siphon tube, abdominal palmate hairs are present, and the larvae rest parallel to the water surface. What is the likely mosquito species?
Options:
A) Culex
B) Anopheles
C) Aedes
D) Mansonia
Correct Answer: B) Anopheles
Question 13
Non-Clinical Question
A study found that breast cancer screening increases the 5-year survival rate, but there is no change in overall mortality. What type of bias does this suggest?
Options:
A) Berksoniana bias
B) Survival bias
C) Lead time bias
D) Detection bias
Correct Answer: C) Lead time bias
Question 14
Non-Clinical Question
During a community medicine demonstration, medical students are instructed to perform the Nalgonda technique. Each student is asked to bring two material bags from the set shown below:
Bag A – Alum
Bag B – Gypsum
Bag C – Charcoal
Bag D – Lime
Which combination of bags is required to perform the Nalgonda technique correctly?
Options:
A) A and D
B) B and C
C) A and B
D) B and C
Correct Answer: A) A and D
Question 15
Clinical Question
A 3-year-old child presents with bowing of the legs. Which of the following nutritional supplementation programs specifically covers children under 6 years of age?
Options:
A) ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services)
B) Mid-Day Meal Scheme
C) Anemia Mukt Bharat
D) National Nutrition Deficiency Control Programme
Correct Answer: A) ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services)
Question 16
Non-Clinical Question
A new community-level intervention is being evaluated. Researchers allocated 20 Primary Health Centres (PHCs) to receive standard care, and another 20 PHCs to receive the new community intervention. What is the most appropriate classification of this study?
Options:
A) Quasi-experimental study
B) Cluster RCT
C) Case-control study
D) Cross-sectional study
Correct Answer: B) Cluster RCT
Question 17
Non-Clinical Question
Which of the following is the most appropriate method used in health planning to assess whether objectives and targets are being fulfilled and to evaluate the quality of outcomes?
Options:
A) Supervision
B) Monitoring
C) Evaluation
D) Planning
Correct Answer: C) Evaluation
Question 18
Non-Clinical Question
A 7-month-old child is on complementary feeding along with continued breastfeeding. The child is given a khatori of semi-solid millet food. What is the recommended frequency and amount per day?
Options:
A) ½ to 1 khatori, 3 times per day
B) ½ to 1 khatori, 4 times per day
C) ½ to 1 khatori, 5 times per day
D) ½ to 1 khatori, 6 times per day
Correct Answer: A) ½ to 1 khatori, 3 times per day
NEET PG 2025 Psychiatry Previous Year Questions
Question 1
A 35-year-old man was arrested for attacking a coworker. During interrogation, he appears dishevelled and expresses paranoid delusions, stating he was not in the right state of mind. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
Options:
A) Release him as he was not in the right state
B) Arrange a psychiatric consultation to assess fitness for trial
C) Proceed to trial
D) Convict him
Correct answer: B) Psychiatric consultation to assess fitness for trial
Question 2
Clinical question
A 68-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer presents with severe dyspnea. The oncology team determines that chemotherapy and radiotherapy would provide no benefit. However, the patient’s daughter insists on “doing everything,” including ICU admission and ventilator support. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
Options:
A) Admit to the ICU and proceed with aggressive management
B) Discharge her as there is no further care that can be provided, and admit her to hospice
C) Start placebo treatment to relieve anxiety
D) Gather a family meeting to assess expectations and patient preferences
Correct answer: D) Gather a family meeting to assess expectations and patient preferences
Question 3
Clinical question
A schizophrenia patient on haloperidol who was responding well for the last 2 years now presents with orofacial dyskinesia, choreiform, tic-like movements, and possible dystonia. What is the most probable diagnosis and appropriate treatment?
Options:
A) Tardive dyskinesia – Valbenazine
B) Akathisia – Propranolol
C) Perioral tremor – Amantadine
D) Acute dystonia – Ropinirole
Correct answer: A) Tardive dyskinesia – Valbenazine
Question 4
Clinical question
A 34-year-old man is brought to the casualty and appears confused. After extensive efforts by a social worker, it was discovered that he is from a nearby village and ended up in the current location after a massive earthquake at his place. He has no recollection of his identity or how he ended up in the current location. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Dissociative amnesia
B) Dissociative personality disorder
C) Dissociative fugue
D) Transient global amnesia
Correct answer: C) Dissociative fugue
Question 5
Clinical question
A 20-year-old girl underwent a traumatic experience two weeks ago after witnessing a road traffic accident and the death of her father. She now experiences flashbacks of the event. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Post-traumatic stress disorder
B) Dissociative disorder
C) Acute stress disorder
D) Major depressive disorder
Correct answer: C) Acute stress disorder
Question 6
Clinical question
An individual comes to the OPD to talk about his friend Mr. K. Mr. K is extremely perfectionistic and often misses deadlines because of this. He has been described as “rigid” since adolescence and is unable to discard items even without sentimental value. Mr. K denies having any problems. Which of the following best describes his personality?
Options:
A) Paranoid personality disorder
B) Narcissistic personality disorder
C) Dependent personality disorder
D) Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
Correct answer: D) Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
Question 7
Clinical question
A patient sitting outside his home believes that whenever a bird is chirping, he has to follow the bird. He believes that he is getting these instructions from God and that he will be harmed if he does not comply. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Sudden delusional idea
B) Delusional perception
C) Delusional reference
D) Visual hallucination
Correct answer: B) Delusional perception
NEET PG 2025 Radiology Previous Year Questions
Q.1
Clinical Question:
A 45-year-old male presented with difficulty swallowing, weight loss, and a chest X-ray showing associated bronchiectasis. The patient undergoes the contrast study shown below. What is the investigation of choice to confirm the diagnosis?
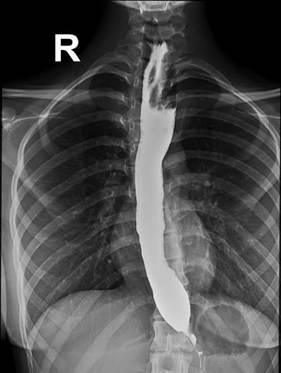
Options:
- Manometry
- CECT chest
- Upper GI endoscopy
- Esophagogram
Correct Answer: A) Manometry
Q.2
Clinical Question:
A 50-year-old male presents with right flank pain. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the abdomen reveals the findings as shown below. Based on the clinical presentation and CT image, what is the most likely diagnosis?
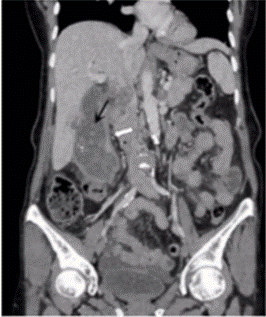
Options:
- Gall bladder cancer
- Renal carcinoma
- Retroperitoneal tumor
- Left lobe liver abscess
Correct Answer: B) Renal carcinoma
Q.3
Clinical Question:
A newborn is admitted to the NICU in the first 24 hours of birth with severe dyspnea/respiratory distress. A chest x-ray is done, which is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
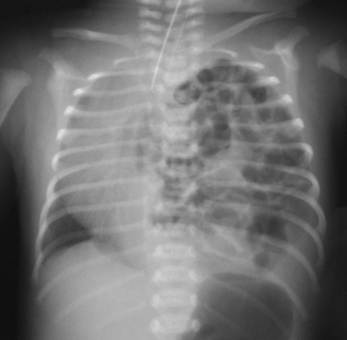
Options:
- Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
- Congenital Pulmonary airway malformation
- Loculated pneumothorax
- Congenital lobar emphysema
Correct Answer: A) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Q.4
Clinical Question:
A 50-year-old male presents with a right-sided neck swelling, which is pulsatile in nature and is compressible, refilling on removal of pressure. A CT-angiogram was performed and is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
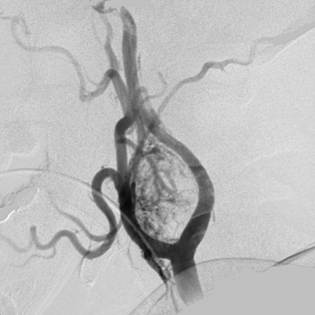
Options:
- Carotid body tumour
- Carotid aneurysm
- AV fistula
- Hemangioma
Correct Answer: A) Carotid body tumour
Q.5
Clinical Question
Identify the correct features of the investigation shown in the given image.
Options:
- Invasive and can be a therapeutic treatment for bladder calculi
- Non-invasive and used to diagnose ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- Non-invasive and gold standard for diagnosing bladder cancer
- Requires percutaneous access to the renal pelvicalyceal system
Correct Answer: B) Non-invasive and used to diagnose ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Q.6
Clinical Question:
A 32-year-old female presents with recurrent headaches, and an MRI brain was done as shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
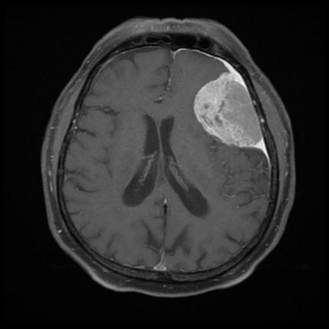
Options:
- Glioma
- Ependymoma
- Meningioma
- Pilocytic astrocytoma
Correct Answer: C) Meningioma
Q.7
Clinical Question:
An 8-year-old presents to the orthopedics OPD with complaints of a painless limp for the past 1 week. An X-ray is done and is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
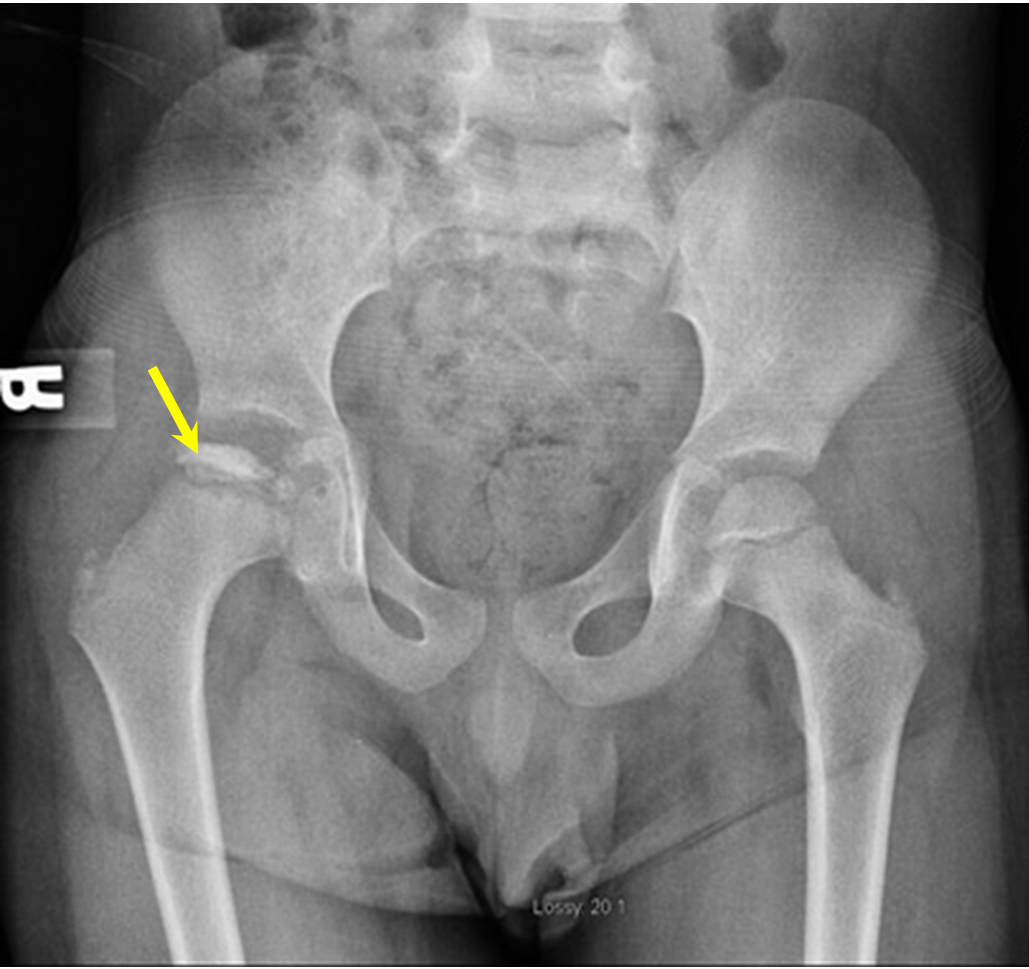
Options:
- Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
- Perthes disease
- D) Tuberculosis hip
Correct Answer: C) Perthes disease
NEET PG 2025 Surgery Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Clinical question
A 65-year-old male with a stab injury to the abdomen presents to the casualty. Examination reveals abdominal tenderness and guarding. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
Options:
A) Peritoneal wash
B) Emergency laparotomy
C) Ultrasound of the abdomen
D) CT abdomen
Correct answer: Emergency laparotomy
Question 2
Clinical question
A 25-year-old with a 5-year history of unilateral varicose veins on the left leg presents to the surgery OPD as shown below. Identify the correct statement regarding this condition.

Options:
A) The most common cause is pelvic tumours
B) Graded as C6
C) Recommended treatment is sclerotherapy in all cases
D) It can lead to eczema and pigmentation
Correct answer: D) It can lead to eczema and pigmentation
Question 3
Clinical question
Identify the stage of breast cancer depicted in the image below.
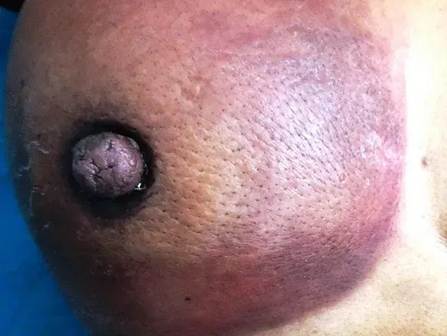
Options:
A) T4b
B) T4d
C) T4c
D) T3
Correct answer: B) T4D
Question 4
Non-clinical question
The fistula marked in the image given below is of which type according to the Park classification?
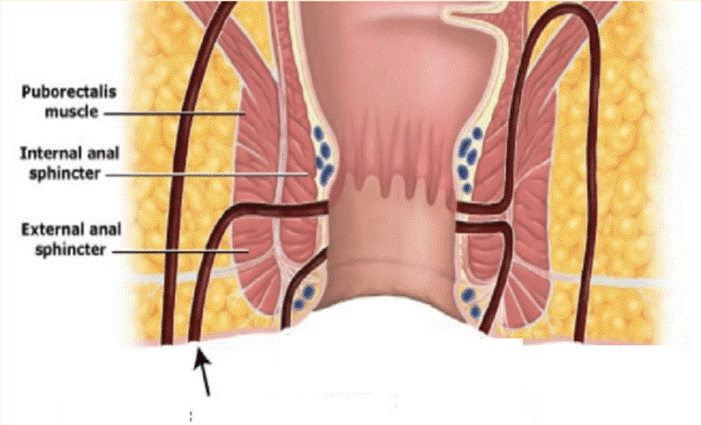
Options:
A) Transsphincteric
B) Intersphincteric
C) Suprasphincteric
D) Extrasphincteric
Correct answer: A) Transsphincteric
Question 5
Non-clinical question
Identify the type of knot shown in the image.
Options:
A) Surgeon’s knot
B) Granny’s knot
C) Square knot
D) Slip knot
Correct answer: A) Surgeon’s knot
Question 6
Non-clinical question
Identify the type of suture material shown in the image
Options:
A) Monofilament
B) Polyfilament
C) Organic
D) Braided
Correct answer: A) Monofilament
Question 7
Clinical question
A 25-year-old patient had an RTA and was initially conscious but later became unconscious and subsequently died. On postmortem examination, multiple petechial haemorrhages were seen in the corpus callosum, but no significant findings were seen on CT brain. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Subarachnoid hemorrhage
B) Diffuse axonal injury
C) Subdural hematoma
D) Extradural hematoma
Options: B) Diffuse axonal injury
Question 8
Non-clinical question
Identify the type of bile duct injury shown in the image based on the Strasberg classification.
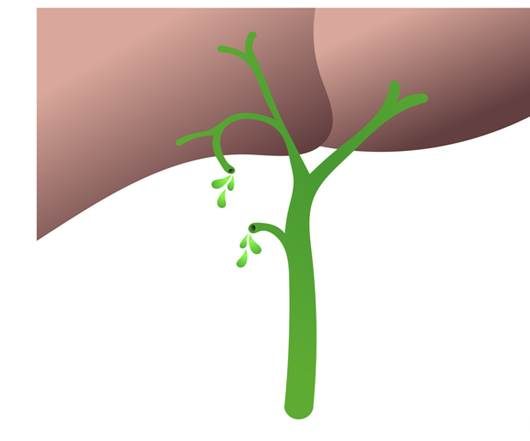
Options:
A) Type A
B) Type B
C) Type C
D) Type D
Correct answer: A) Type A
Question 9
Clinical question
A patient with jaundice, anorexia, and weight loss for 2 months. The gall bladder is palpable, soft, and non-tender. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Options:
A) Hepatocellular carcinoma
B) Gall bladder cancer
C) Pancreatic head cancer
D) Choledocholithiasis
Correct answer: C) Pancreatic head cancer
Question 10
Clinical question
A 40-year-old had the following structure resected. Which of the following complications can be seen 4 days later?
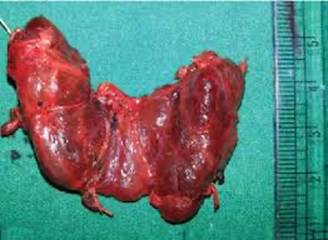
Options:
A) Deviation of the angle of the mouth
B) Carpopedal spasm
C) Neck hematoma
D) Migratory thrombophlebitis
Correct answer: B) Carpopedal spasm
Question 11
Non-clinical question
What is true about the procedure shown in the image?
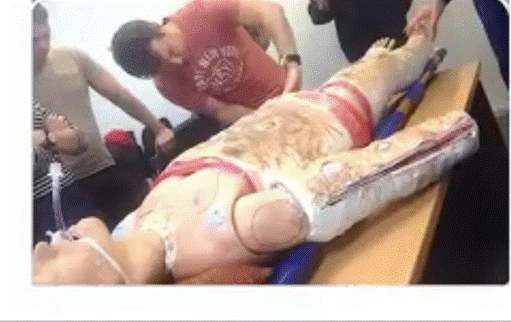
Options:
A) Done in circumferential burns
B) The image shows a skin graft
C) Done for quick healing
D) Incisions on the upper limb are done to avoid major vessels
Correct answer: A) Done in circumferential lesions
Question 12
Clinical question
A 7-year-old boy presents with progressive non-retractable foreskin and tense, white preputial skin. What is the diagnosis?
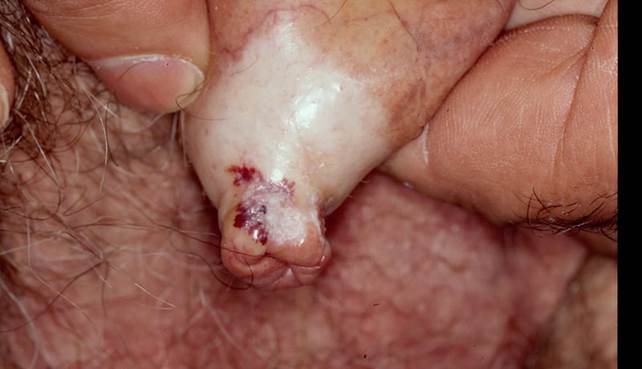
Options:
A) Recurrent balanoposthitis
B) Urethral meatus stenosis
C) Paraphimosis
D) Balanitis xerotica obliterans
Correct answer: D) Balanitis xerotica obliterans
Commonly Asked Questions about NEET PG PYQs
1. Why should I practice NEET PG Previous Year Questions (PYQs)?
Practicing PYQs helps you understand the exam’s structure, focus areas, and level of difficulty. It also sharpens problem-solving skills and improves time management.
2. How many years of NEET PG PYQs should I solve?
It’s best to solve at least the last 5–7 years of PYQs. This gives you a clear view of recurring patterns and important subjects.
3. Are PYQs alone enough to crack NEET PG?
No. PYQs are a valuable revision tool, but should be combined with standard textbooks, conceptual study, and mock tests for complete preparation.
4. When should I start solving PYQs?
You can start early after finishing basic concepts, but they’re especially useful during revision phases. Multiple revisions of PYQs enhance recall and confidence.
5. Do NEET PG questions repeat from previous years?
Exact questions rarely repeat, but concepts and themes often do. Practicing PYQs ensures you don’t miss out on these recurring areas.
6. How do PYQs improve performance on exam day?
By solving PYQs in a timed setting, you get familiar with the exam format, manage stress better, and reduce last-minute surprises.
7. Where can I download previous years’ questions from?
Instead of searching multiple platforms for PYQs, get it all in one place with DocTutorials. Our QBank of 12,000+ MCQs, including PYQs, gives you exactly what you need to master the exam.
8. Will I get solutions for the NEET PG question papers?
With DocTutorials V5 QBank, all 12,000+ MCQs & IBQs come with clear, exam-oriented explanations for both correct and incorrect options, integrated with concepts and PYQs—ensuring deep conceptual clarity, better pattern recognition, and fewer repeat mistakes
Latest Blogs
-

NEET SS Exam 2024: Analysis, Key Dates, Counselling
The NEET SS 2024 exam kicked off on March 29, 2025. Over two days and two slots, candidates across 13…
-

NEET PG Registration 2025: An Essential Guide For Exam Prep
The NEET PG registration, which is conducted online, is a crucial step in the exam process. Filling out the NEET…
-

NEET PG Syllabus 2026: A Must-Have Complete Guide for Exam Success
The NEET PG Syllabus acts as one of the foundation stones for aspiring postgraduate medical students like you who are…
-

NEET PG Exam 2025- Date, Pattern, Marking Scheme, Subject Wise Weightage, and Exam Mode
NEET PG Exam 2025 is the ultimate gateway for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses in medicine, including MD,…
-

FMGE Exam 2025: Date, Eligibility, Application, Syllabus, and Exam Pattern
The Foreign Medical Graduate Examination (FMGE), slated for 2025, remains a pivotal assessment for foreign medical graduates aspiring to practice…
-

INI SS Topper: 1 Dream, 1 Study Buddy, 1 Rank – The Journey of Dr. Prithivi Raaj, CML 1 & (AIIMS) AML 1 in DM Cardiology
Achieving the top rank in a competitive exam like the INI SS DM Cardiology requires tireless dedication, a structured approach,…
-

9 Essential MBBS Preparation Tips for Success
Achieving the dream of becoming a doctor is not easy. You need to be determined and have the right mindset…
-

INI SS Results: Merit List, Exam Insights, and What Comes Next
The INI SS results for October 2024 are just around the corner. This is a life-changing moment for thousands of…
-

INI CET Exam 2025: Your Roadmap to Success – Key Topics, Strategies, and Lessons from Last Year’s Papers
The INI CET exam is more than just a test; it’s a significant milestone for many medical students aiming to…
-

INI CET Exam Success: Previous Year Question Papers & Ultimate Guide – INI CET PYQ
One can feel overwhelmed while preparing for the INI CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test). A vast syllabus,…