Earwax Blockage: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, and Treatment
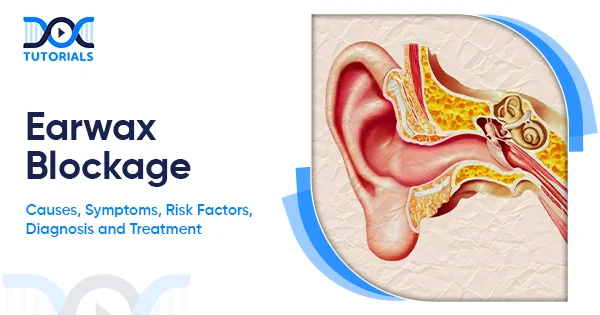
Human beings rely on five primary sense organs, and the ear is one of them. It plays a critical role in both hearing and maintaining balance. The glands in the ear canal secrete an oily wax that keeps our ears clean by trapping dirt and germs.
However, when the amount of secretion exceeds the normal level, it can block the ear canal. This leads to earwax blockage. Keep on reading to learn about earwax blockage, its causes and symptoms, and the associated treatment.
What is Earwax Blockage?
When the earwax builds up in the ears beyond the normal amount, causing itching, ear pain, and other issues, it is known as an earwax blockage.
Medically known as “Cerumen Impaction”, earwax blockage is a condition in which the cerumen builds up in the ear beyond normal levels, blocking the ear canals and causing ear pain and itching. In severe cases, earwax blockage can cause hearing loss if left untreated.
Cerumen, or earwax, is a waxy oil that is produced by the glands present in the ear canal that help to keep the inner ear clean and protect it from infections.
Who is at Risk of Developing Earwax Blockage?
Anyone can develop an earwax blockage; however, people with certain conditions, such as hypertrichosis, developmental disabilities, eczema, misshapen ear canals, etc., are more prone to ceruminous impaction.
Earwax blockage can happen to anyone, regardless of age or gender. However, it is more commonly seen in children, affecting 10% children and 5% adults. The following section lists the people who are more prone towards developing earwax blockage:
- People with hypertrichosis or hairy ears.
- People who use foreign bodies, such as cotton swabs or other sharp objects, to clean their ears.
- People above the age of 55.
- People using hearing aids or earplugs.
- People with developmental disabilities.
- People with skin conditions like Eczema.
- People with misshapen ear canals.
What are the Causes and Risk Factors of Earwax Blockage?
Some causes of earwax blockage include hypertrichosis, hard ceruminous debris, narrow ear canals, and the regular use of foreign bodies to clean the ear. Apart from these, risk factors such as recurrent ear infections also contribute to cerumen impaction.
The majority of people suffer from earwax blockage only because their glands naturally produce more cerumen. However, some other causes of cerumen impaction are:
- Having hard cerumen
- Having hairy ears
- Having narrow ear canals
- Wearing earplugs and hearing aids
- Putting cotton swabs into the ears regularly
Apart from the causes, certain risk factors make people prone towards impacted cerumen, such as:
- Bony growths or osteomas
- Recurrent ear infections
- Frequent exposure to water
- Males are at a higher risk than females
- Psoriasis or dermatitis
What are the Symptoms and Diagnosis of Earwax Blockage?
The symptoms of earwax blockage include ear pain, hearing loss, ear itching, dizziness, and a feeling of fullness, which help diagnose the condition. The physician also uses an otoscope to examine the buildup of cerumen.
The primary symptom of earwax blockage is ear pain, which may or may not be associated with the following symptoms:
- Ear ache
- A feeling of fullness in the ears
- Hearing loss, where the condition deteriorates over time
- Ringing in the ears or tinnitus
- Itching in the ears
- Discharge from the ear
- Dizziness
- Ear infections
Earwax blockage is diagnosed based on the above symptoms and a few other tests that are mentioned below:
- Complete physical examination, including the Weber and Rinne tests.
- An ear examination by the physician using an otoscope to check the amount of wax buildup.
What are the Treatment Options for Earwax Blockage?
Earwax blockage can be treated at home using earwax-dissolving solutions and ear irrigation, and at healthcare centres by trained staff.
Earwax blockage, if not treated in time, can cause hearing loss that worsens over time. Go through the following section to learn about the several methods to treat cerumen impaction at home:
- Regular and Proper Cleaning of Ears: Use a washcloth to clean the outer area of your ear, and don’t forget to dry your ears after a shower properly. Don’t use sharp objects or safety pins to clean your ears.
- Use Earwax-Dissolving Solutions: Using cerumenolytic solutions such as glycerin, mineral oil, baby oil, or saline helps soften hard impacted earwax. These solutions should be applied sparingly to the affected ear by lying on the opposite side.
- Ear Irrigation: After softening the earwax with cerumenolytic solutions, use a syringe to rinse the ear with water or saline, then gently irrigate with a bulb syringe.
- In-office Earwax Removal: If the impaction is severe, visit your nearest healthcare centre, and the physician will remove it using special instruments such as a cerumen spoon, forceps, or a suction device.
What is the Prognosis of Earwax Blockage?
The prognosis for earwax blockage is good if treated promptly, but if left untreated, the person may suffer from severe infection and pain.
Once cleared, the person may again suffer from earwax blockage, and the hearing loss is temporary and partial. Hearing returns gradually after the impaction is cleared. People using hearing aids should get themselves checked every 3 to 6 months.
FAQs about Earwax Blockage
- How do you unblock a waxed ear?
Soften the earwax with the ceruminolytic ear drops, then clean the ear with gentle irrigation.
- Will the earwax blockage clear on its own?
Asymptomatic earwax blockage can clear on its own, but ceruminous impaction with clinical manifestations requires intervention by a skilled healthcare professional.
- How can I tell if I have an earwax blockage?
Some of the signs and symptoms of earwax blockage are:
- Earache
- Ringing or noises in the ear
- Dizziness
- Decreased hearing
- Coughing
- Is earwax removal painful?
No, earwax removal is not painful if performed correctly by a skilled staff member.
- How does a doctor remove earwax?
If the condition is severe, the doctor uses special instruments, such as a ceruminolytic spoon, suction, or forceps, to remove earwax.
Conclusion
Impacted earwax is a minor ailment that can worsen over time if left untreated. If not treated or cleared on time, the earwax blockage can cause a severe earache or infection that may lead to permanent hearing loss.
Maintain hygiene and keep your ears clean and healthy to prevent other chronic ear diseases that may affect your hearing and balance.
To understand more such complex NEET PG concepts easily, join DocTutorials today and explore our NEET PG course to excel in your career!
Latest Blogs
-

9 Essential MBBS Preparation Tips for Success
Achieving the dream of becoming a doctor is not easy. You need to be determined and have the right mindset…



