Mitral Stenosis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
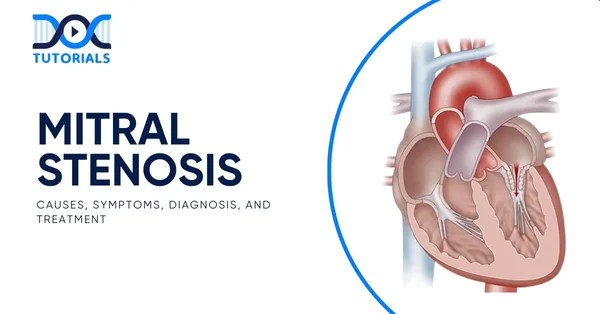
Mitral stenosis is a heart disorder which constricts the mitral valve and makes the flow of blood between the left atrium and the left ventricle difficult. This may cause complications with atrial fibrillation, stroke, or heart failure if it is not treated. Early diagnosis and follow-up care help manage the condition through medical procedures.
If you are appearing for the NEET PG exam, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of mitral stenosis, since it is essential for accurate clinical judgement and effective patient care.
Read on to explore this topic in detail.
What is Mitral Stenosis?
Mitral stenosis is a condition in which the mitral valve inside the heart becomes narrowed. Over time, this restriction in blood flow can lead to irregular heart rhythms, an increased risk of stroke, and may result in heart failure or death.
Narrowing of the mitral valve causes obstruction in the flow of blood between the left upper chamber (atrium) and the left lower chamber (ventricle) of the heart. This is due to the fact that the flow of blood is restricted since the valve is not opened completely.
The mitral valve plays a critical role as the first valve blood encounters after returning from the lungs with oxygen. Proper blood flow into the left ventricle is essential, as this chamber pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body’s tissues and organs.
What are the Causes of Mitral Stenosis?
The following are the causes of mitral stenosis:
- Rheumatic Fever
This is the most frequent cause of mitral stenosis. It often follows untreated or poorly managed strep throat. The condition leads to scarring and deformity of the mitral valve, known as rheumatic mitral valve disease.
- Calcium Build-up
As a person ages, calcium can deposit itself around the mitral valve ring (annulus), resulting in a condition commonly known as mitral annular calcification (MAC). When severe, this can restrict valve movement and cause symptoms of stenosis.
- Congenital Heart Defects
In extreme cases, infants are found to be born with a narrowed mitral valve. This type of mitral stenosis is acquired at birth, and it develops as a result of the disturbed formation of the valves during gestation.
- Autoimmune Conditions
Disorders such as lupus may occasionally lead to inflammation and thickening of the mitral valve, contributing to stenosis. However, this cause is quite uncommon.
- Radiation Exposure to the Chest
Cancer treatments involving chest radiation can result in long-term thickening and stiffening of the mitral valve. These changes usually manifest two to three decades after therapy.
What are the Symptoms of Mitral Stenosis?
Mitral valve stenosis can lead to a range of symptoms, often developing gradually over time. Common signs include:
- Hoarse Voice
Increased pressure in the upper chamber of the heart can affect the nerve that controls the vocal cords, leading to changes in an individual’s voice.
- Breathlessness
This is the most frequent symptom. It tends to happen during physical exertion or while lying flat, due to increased pressure in the lungs.
- Heart Palpitations
An individual may feel an abnormal or racing heartbeat. This usually results from atrial fibrillation, a condition caused by the increased strain on the heart’s upper left chamber.
- Frequent Bouts of Bronchitis
People with mitral stenosis may experience repeated respiratory infections as a result of poor blood flow and pressure build-up in the lungs.
- Stroke
Reduced blood flow in the upper chambers can lead to clot formation. If a clot travels to the brain, it may block a blood vessel and trigger a stroke.
- Coughing Up Blood
In some cases, pressure on the lung blood vessels can cause small blood vessels to burst, leading to blood in the cough.
- Swelling of the Ankles, Feet, or Abdomen
When the heart’s pumping ability weakens, fluid may accumulate in various parts of the body, especially the lower limbs and abdomen.
- Extreme Fatigue
More than simple tiredness, this refers to an exhaustion that affects an individual’s ability to carry out everyday tasks.
What is the Diagnosis of Mitral Stenosis?
To confirm mitral stenosis and assess how severe it is, a cardiologist may carry out one or more of the following diagnostic tests:
- Exercise Stress Test
This involves physical activity such as walking on a treadmill or cycling on a stationary bike while monitoring heart function. The test shows how the heart performs under stress and whether symptoms of valve disease appear during exercise. If physical activity is not possible, certain medications can be used to simulate the effects of exercise on the heart.
- Echocardiogram
This is one of the primary tools used to identify mitral stenosis. It uses sound waves to produce moving images of the heart. The scan reveals blood flow issues and valve abnormalities, and helps determine the extent of narrowing in the mitral valve.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
This test records the heart’s electrical signals through sensors placed on the chest. It helps detect irregular heart rhythms that may be associated with mitral valve stenosis.
- Chest X-ray
X-ray pictures of the lungs and the heart can give information on whether the heart is enlarged, which is an indication of valve disease.
- Cardiac CT Scan
A cardiac CT (computed tomography) scan can provide detailed cardiac structure images, including the heart valves, through the combination of several X-ray images. It is especially helpful in detecting cases of mitral stenosis that are not due to rheumatic fever.
- Cardiac MRI
This MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan employs magnetic fields and radio waves to generate high-resolution images of the heart. It can help measure how severely the mitral valve is narrowed.
- Cardiac Catheterisation
During this process, a narrow tube will be placed in one of the blood vessels and directed to the heart. It provides a direct way to measure pressures in the heart chambers and can therefore aid in the making of a diagnosis of mitral stenosis and how severe it is.
What are the Treatment Options for Mitral Stenosis?
Treatment of mitral stenosis varies with the severity of the problem and the symptoms one develops. They include:
- Medications
Doctors can prescribe medication when the symptoms develop to manage them. Although these medicines do not correct the narrowed valve, they can reduce the strain on the heart and alleviate discomfort. Some common medicines are:
- Anticoagulants: They lower the risk of blood clot formation, especially when there is a case of atrial fibrillation.
- Diuretics: They help to remove excess fluid by increasing urine output, which helps to ease pressure on the lungs and heart.
- Antiarrhythmics: They are used in the stabilisation of abnormal heart rhythms, which might arise due to the presence of mitral stenosis.
- Beta-blockers: These reduce the heart rate, allowing more time for the heart chambers to fill properly.
- Balloon Valvuloplasty
When medication is insufficient but the valve is not too severely damaged, a balloon valvuloplasty may be recommended. This minimally invasive procedure involves threading a catheter with a balloon tip through a vein to reach the heart. Once in place within the narrowed mitral valve, the balloon is inflated to enlarge the valve opening.
- Surgical Intervention
There are 2 main surgical procedures used to treat mitral valve stenosis:
- Mitral Valve Replacement
Most often, the mitral valve has to be replaced. The replacement valve may be mechanical, which is made from durable materials like metal and carbon, or biological, which is made from animal tissue such as that of a pig or cow.
- Mitral Valve Repair
Wherever suitable, surgeons may attempt to preserve the existing valve. This involves carefully separating the valve leaflets and enlarging the narrowed opening. Nevertheless, this method is taken into account only under certain conditions where the structure of the valve can be effectively repaired.
FAQs About Mitral Stenosis
- What is mitral stenosis?
Mitral stenosis is the narrowing of the mitral valve, which restricts blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart.
- How is mitral stenosis diagnosed?
Tests done to diagnose mitral stenosis include echocardiogram, ECG, chest X-ray, cardiac CT or MRI scan, stress test, and cardiac catheterisation.
- Is surgery always necessary for mitral stenosis treatment?
No, surgery is not always necessary for mitral stenosis treatment. The mild cases can be restricted only to medication and supervision. Surgery is considered when symptoms worsen or when the valve is so narrow.
Conclusion
A proper understanding of mitral stenosis, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment is important in clinical practice and academic performance. Early diagnosis and proper management play a vital role in preventing serious complications and improving patient outcomes.
Being a NEET PG aspirant, one should ace this topic, as it will enhance clinical reasoning and help you tackle complex cardiac cases with a lot of assurance. DocTutorials provides comprehensive learning resources such as high-yield video lectures, concise notes, expert-led discussions, and more.
Start exploring our NEET PG course today and take a step towards achieving the dream rank.
Latest Blogs
-

9 Essential MBBS Preparation Tips for Success
Achieving the dream of becoming a doctor is not easy. You need to be determined and have the right mindset…




